Aspirin Inhibits Fibronectin Expression and Reverses Fibronectin-Mediated Cell Invasiveness by Activating Akt Signaling in Preeclampsia
- PMID: 36558974
- PMCID: PMC9781454
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15121523
Aspirin Inhibits Fibronectin Expression and Reverses Fibronectin-Mediated Cell Invasiveness by Activating Akt Signaling in Preeclampsia
Abstract
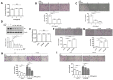
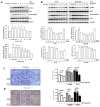
Preeclampsia is a severe gestational hypertensive disorder that may lead to maternal multiple organ dysfunction and adverse fetal outcomes. Aspirin provides a protective effect by reducing the risk of preeclampsia; however, its mechanism of action is unclear. Fibronectin (FN) is a key factor in cell motility and is associated with preeclampsia. Here, we demonstrated that cellular FN expression was elevated in the placenta of preeclamptic patients. The functional roles of plasma and cellular FN in trophoblasts were investigated by treating HTR-8/SVneo cells with exogenous recombinant human FN protein (rhFN) and siRNA, respectively. Trophoblast migration and invasion were inhibited by rhFN and facilitated by FN knockdown. Moreover, rhFN activated ERK and Akt signaling in trophoblasts, and FN-suppressed cell motility was rescued by ERK and/or Akt inhibitors. In this study, aspirin suppressed trophoblast cellular FN expression and reversed FN-mediated cell functions, including cell migration, invasion, and ERK/Akt signal changes. Taken together, the results of this study revealed the effects of FN on trophoblast motility and signaling; aspirin inhibits FN expression and reverses FN-mediated trophoblast biology. These results provide a drug mechanism for disease prevention and a target for preeclampsia intervention.
Keywords: Akt; aspirin; fibronectin; preeclampsia; trophoblast invasion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

