Aptamers as Smart Ligands for Targeted Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 36559056
- PMCID: PMC9781707
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122561
Aptamers as Smart Ligands for Targeted Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy
Abstract
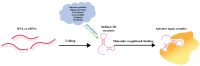
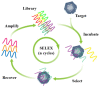
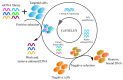
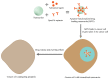
Undesirable side effects and multidrug tolerance are the main holdbacks to the treatment of cancer in conventional chemotherapy. Fortunately, targeted drug delivery can improve the enrichment of drugs at the target site and reduce toxicity to normal tissues and cells. A targeted drug delivery system is usually composed of a nanocarrier and a targeting component. The targeting component is called a "ligand". Aptamers have high target affinity and specificity, which are identified as attractive and promising ligands. Therefore, aptamers have potential application in the development of smart targeting systems. For instance, aptamers are able to efficiently recognize tumor markers such as nucleolin, mucin, and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Besides, aptamers can also identify glycoproteins on the surface of tumor cells. Thus, the aptamer-mediated targeted drug delivery system has received extensive attention in the application of cancer therapy. This article reviews the application of aptamers as smart ligands for targeted drug delivery in cancer therapy. Special interest is focused on aptamers as smart ligands, aptamer-conjugated nanocarriers, aptamer targeting strategy for tumor microenvironment (TME), and aptamers that are specified to crucial cancer biomarkers for targeted drug delivery.
Keywords: aptamers; cancer therapy; drug delivery; smart ligands; targeted.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aptamers as Versatile Ligands for Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Feb 17;15:1059-1071. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S237544. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32110008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smart ligand: aptamer-mediated targeted delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs and siRNA for cancer therapy.J Control Release. 2013 Oct 28;171(2):152-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.06.006. Epub 2013 Jun 15. J Control Release. 2013. PMID: 23777885 Review.
-
Tumor-Specific Delivery of 5-Fluorouracil-Incorporated Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Targeted Aptamers as an Efficient Treatment in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Models.Gastroenterology. 2021 Sep;161(3):996-1010.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.05.055. Epub 2021 Jun 25. Gastroenterology. 2021. PMID: 34097885
-
Aptamers and nanobodies as alternatives to antibodies for ligand-targeted drug delivery in cancer.Drug Discov Today. 2023 May;28(5):103550. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2023.103550. Epub 2023 Mar 10. Drug Discov Today. 2023. PMID: 36906220 Review.
-
Recent development of aptamer conjugated chitosan nanoparticles as cancer therapeutics.Int J Pharm. 2022 May 25;620:121751. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121751. Epub 2022 Apr 15. Int J Pharm. 2022. PMID: 35436511 Review.
Cited by
-
Multifunctional Polymeric Biodegradable and Biocompatible Coatings Based on Silver Nanoparticles: A Comparative In Vitro Study on Their Cytotoxicity towards Cancer and Normal Cell Lines of Cytostatic Drugs versus Essential-Oil-Loaded Nanoparticles and on Their Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activities.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jul 4;15(7):1882. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071882. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37514068 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidics engineering towards personalized oncology-a review.In Vitro Model. 2023 Jul 13;2(3-4):69-81. doi: 10.1007/s44164-023-00054-z. eCollection 2023 Aug. In Vitro Model. 2023. PMID: 39871996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fast assembly of 'clickable nanogels' for drug delivery.Nanoscale Adv. 2025 Aug 8;7(17):5421-5434. doi: 10.1039/d5na00471c. eCollection 2025 Aug 19. Nanoscale Adv. 2025. PMID: 40786133 Free PMC article.
-
Analytical Techniques for Characterizing Tumor-Targeted Antibody-Functionalized Nanoparticles.Life (Basel). 2024 Apr 10;14(4):489. doi: 10.3390/life14040489. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38672759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imiquimod-Loaded Nanosystem for Treatment Human Papillomavirus-Induced Lesions.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jun 27;16(7):864. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070864. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39065561 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Valtorta S., Salvatore D., Rainone P., Belloli S., Bertoli G., Moresco R.M. Molecular and cellular complexity of glioma. Focus on tumour microenvironment and the use of molecular and imaging biomarkers to overcome treatment resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:5631. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165631. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

