Cannabidiol Loaded Topical Ophthalmic Nanoemulsion Lowers Intraocular Pressure in Normotensive Dutch-Belted Rabbits
- PMID: 36559077
- PMCID: PMC9781840
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122585
Cannabidiol Loaded Topical Ophthalmic Nanoemulsion Lowers Intraocular Pressure in Normotensive Dutch-Belted Rabbits
Abstract
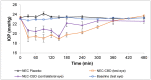
Cannabidiol (CBD) is the major non-psychoactive and most widely studied of the cannabinoid constituents and has great therapeutic potential in a variety of diseases. However, contradictory reports in the literature with respect to CBD's effect on intraocular pressure (IOP) have raised concerns and halted research exploring its use in ocular therapeutics. Therefore, the current investigation aimed to further evaluate CBD's impact on the IOP in the rabbit model. CBD nanoemulsions, containing Carbopol® 940 NF as a mucoadhesive agent (CBD-NEC), were prepared using hot-homogenization followed by probe sonication. The stability of the formulations post-moist-heat sterilization, in terms of physical and chemical characteristics, was studied for three different storage conditions. The effect of the formulation on the intraocular pressure (IOP) profile in normotensive Dutch Belted male rabbits was then examined. The lead CBD-NEC formulation (1% w/v CBD) exhibited a globule size of 259 ± 2.0 nm, 0.27 ± 0.01 PDI, and 23.2 ± 0.4 cP viscosity, and was physically and chemically stable for one month (last time point tested) at 4 °C, 25 °C, and 40 °C. CBD-NEC significantly lowered the IOP in the treated eyes for up to 360 min, with a peak drop in IOP of 4.5 mmHg observed at the 150 min time point, post-topical application. The IOP of the contralateral eye (untreated) was also observed to be lowered significantly, but the effect lasted up to the 180 min time point only. Overall, topically administered CBD, formulated in a mucoadhesive nanoemulsion formulation, reduced the IOP in the animal model studied. The results support further exploration of CBD as a therapeutic option for various inflammation-based ocular diseases.
Keywords: IOP; autoclave; cannabidiol; carbopol® 940 NF; nanoemulsion; rabbits.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of mucoadhesive agent inclusion on the intraocular pressure lowering profile of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol-valine-hemisuccinate loaded nanoemulsions in New Zealand white rabbits.Int J Pharm. 2022 Mar 25;616:121564. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121564. Epub 2022 Feb 11. Int J Pharm. 2022. PMID: 35151817
-
Formulation and In Vitro-Ex vivo Evaluation of Cannabidiol and Cannabidiol-Valine-Hemisuccinate Loaded Lipid-Based Nanoformulations for Ocular Applications.Int J Pharm. 2024 May 25;657:124110. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.124110. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Int J Pharm. 2024. PMID: 38604539
-
The dose-dependent effect of a stabilized cannabidiol nanoemulsion on ocular surface inflammation and intraocular pressure.Int J Pharm. 2022 Apr 5;617:121627. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121627. Epub 2022 Mar 1. Int J Pharm. 2022. PMID: 35245638
-
Molecular Targets of Cannabidiol in Neurological Disorders.Neurotherapeutics. 2015 Oct;12(4):699-730. doi: 10.1007/s13311-015-0377-3. Neurotherapeutics. 2015. PMID: 26264914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cannabidiol Adverse Effects and Toxicity.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2019;17(10):974-989. doi: 10.2174/1570159X17666190603171901. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31161980 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cannabinoid-Based Ocular Therapies and Formulations.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Mar 27;15(4):1077. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041077. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginger Oil Nanoemulsion Formulation Augments Its Antiproliferative Effect in Ehrlich Solid Tumor Model.Foods. 2023 Nov 15;12(22):4139. doi: 10.3390/foods12224139. Foods. 2023. PMID: 38002196 Free PMC article.
-
Silk Fibroin Formed Bioadhesive Ophthalmic Gel for Dry Eye Syndrome Treatment.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Apr 29;25(5):92. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02792-z. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 38684590
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Efficacy of Topical Dosage Forms Containing Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System Loaded with Curcumin.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jul 31;15(8):2054. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15082054. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37631267 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticles in Ocular Drug Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jun 8;15(6):1675. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15061675. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37376123 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liou G.I., Auchampach J.A., Hillard C.J., Zhu G., Yousufzai B., Mian S., Khan S., Khalifa Y. Mediation of Cannabidiol Anti-Inflammation in the Retina by Equilibrative Nucleoside Transporter and A2A Adenosine Receptor. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008;49:5526–5531. doi: 10.1167/iovs.08-2196. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous