Trends in Drug Delivery Systems for Natural Bioactive Molecules to Treat Health Disorders: The Importance of Nano-Liposomes
- PMID: 36559301
- PMCID: PMC9785269
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122808
Trends in Drug Delivery Systems for Natural Bioactive Molecules to Treat Health Disorders: The Importance of Nano-Liposomes
Abstract
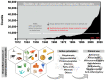
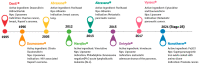
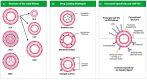
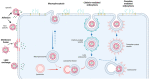
Drug delivery systems are believed to increase pharmaceutical efficacy and the therapeutic index by protecting and stabilizing bioactive molecules, such as protein and peptides, against body fluids' enzymes and/or unsuitable physicochemical conditions while preserving the surrounding healthy tissues from toxicity. Liposomes are biocompatible and biodegradable and do not cause immunogenicity following intravenous or topical administration. Still, their most important characteristic is the ability to load any drug or complex molecule uncommitted to its hydrophobic or hydrophilic character. Selecting lipid components, ratios and thermo-sensitivity is critical to achieve a suitable nano-liposomal formulation. Nano-liposomal surfaces can be tailored to interact successfully with target cells, avoiding undesirable associations with plasma proteins and enhancing their half-life in the bloodstream. Macropinocytosis-dynamin-independent, cell-membrane-cholesterol-dependent processes, clathrin, and caveolae-independent mechanisms are involved in liposome internalization and trafficking within target cells to deliver the loaded drugs to modulate cell function. A successful translation from animal studies to clinical trials is still an important challenge surrounding the approval of new nano-liposomal drugs that have been the focus of investigations. Precision medicine based on the design of functionalized nano-delivery systems bearing highly specific molecules to drive therapies is a promising strategy to treat degenerative diseases.
Keywords: liposomal formulations; liposomal marketed formulations; liposome–cell interaction; nano-delivery systems; protein and peptide encapsulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Liposomal drug delivery systems: an update review.Curr Drug Deliv. 2007 Oct;4(4):297-305. doi: 10.2174/156720107782151269. Curr Drug Deliv. 2007. PMID: 17979650 Review.
-
New drug candidates for liposomal delivery identified by computer modeling of liposomes' remote loading and leakage.J Control Release. 2017 Apr 28;252:18-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.02.015. Epub 2017 Feb 16. J Control Release. 2017. PMID: 28215669
-
Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the future of chemotherapy.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015 Jun;93:52-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.03.018. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015. PMID: 25813885 Review.
-
The liposomal formulation of doxorubicin.Methods Enzymol. 2005;391:71-97. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)91004-5. Methods Enzymol. 2005. PMID: 15721375
-
Liposomal formulations of carboplatin injected by convection-enhanced delivery increases the median survival time of F98 glioma bearing rats.J Nanobiotechnology. 2018 Oct 5;16(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s12951-018-0404-8. J Nanobiotechnology. 2018. PMID: 30290821 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nanoliposomes Permeability in a Microfluidic Drug Delivery Platform across a 3D Hydrogel.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jun 4;16(6):765. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16060765. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38931887 Free PMC article.
-
Global Advancements in Bioactive Material Manufacturing for Drug Delivery: A Comprehensive Study.ACS Omega. 2025 Jan 3;10(1):1207-1225. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c08669. eCollection 2025 Jan 14. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 39829510 Free PMC article.
-
Antiproliferative Effect of Methanolic Extract of Vernonia greggii (Asteraceae) on Human Tumoral HeLa Cells Nanoencapsulated into PLGA-Nanoparticles.Materials (Basel). 2025 Jan 27;18(3):580. doi: 10.3390/ma18030580. Materials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39942246 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional Liposomes Co-Modified with Ginsenoside Compound K and Hyaluronic Acid for Tumor-Targeted Therapy.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Feb 1;16(3):405. doi: 10.3390/polym16030405. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38337294 Free PMC article.
-
Exploiting Natural Niches with Neuroprotective Properties: A Comprehensive Review.Nutrients. 2024 Apr 26;16(9):1298. doi: 10.3390/nu16091298. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38732545 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Süntar I. Importance of ethnopharmacological studies in drug discovery: Role of medicinal plants. Phytochem. Rev. 2020;19:1199–1209. doi: 10.1007/s11101-019-09629-9. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

