Expandable Drug Delivery Systems Based on Shape Memory Polymers: Impact of Film Coating on Mechanical Properties and Release and Recovery Performance
- PMID: 36559306
- PMCID: PMC9786903
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122814
Expandable Drug Delivery Systems Based on Shape Memory Polymers: Impact of Film Coating on Mechanical Properties and Release and Recovery Performance
Abstract
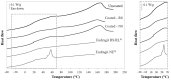
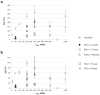
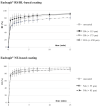
Retentive drug delivery systems (DDSs) are intended for prolonged residence and release inside hollow muscular organs, to achieve either local or systemic therapeutic goals. Recently, formulations based on shape memory polymers (SMPs) have gained attention in view of their special ability to recover a shape with greater spatial encumbrance at the target organ (e.g., urinary bladder or stomach), triggered by contact with biological fluids at body temperature. In this work, poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA), a pharmaceutical-grade SMP previously shown to be an interesting 4D printing candidate, was employed to fabricate expandable organ-retentive prototypes by hot melt extrusion. With the aim of improving the mechanical resistance of the expandable DDS and slowing down relevant drug release, the application of insoluble permeable coatings based on either Eudragit® RS/RL or Eudragit® NE was evaluated using simple I-shaped specimens. The impact of the composition and thickness of the coating on the shape memory, swelling, and release behavior as well as on the mechanical properties of these specimens was thoroughly investigated and the effectiveness of the proposed strategy was demonstrated by the results obtained.
Keywords: expandable drug delivery system; film-coating; fused deposition modeling; hot melt extrusion; poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA); retentive drug delivery system; shape memory polymer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Insights into the Safety and Versatility of 4D Printed Intravesical Drug Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 24;15(3):757. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15030757. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36986618 Free PMC article.
-
Expandable drug delivery system for gastric retention based on shape memory polymers: Development via 4D printing and extrusion.Int J Pharm. 2019 Nov 25;571:118700. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118700. Epub 2019 Sep 14. Int J Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31526838
-
Retentive device for intravesical drug delivery based on water-induced shape memory response of poly(vinyl alcohol): design concept and 4D printing feasibility.Int J Pharm. 2019 Mar 25;559:299-311. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.01.045. Epub 2019 Jan 30. Int J Pharm. 2019. PMID: 30707934
-
Shape memory materials and 4D printing in pharmaceutics.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021 Jun;173:216-237. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.03.013. Epub 2021 Mar 25. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021. PMID: 33774118 Review.
-
Coupling hot melt extrusion and fused deposition modeling: Critical properties for successful performance.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021 May;172:52-63. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.02.006. Epub 2021 Feb 9. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021. PMID: 33571550 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into the Safety and Versatility of 4D Printed Intravesical Drug Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 24;15(3):757. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15030757. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36986618 Free PMC article.
-
Untethered shape-changing devices in the gastrointestinal tract.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2023 Jul-Dec;20(12):1801-1822. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2023.2291450. Epub 2023 Dec 29. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2023. PMID: 38044866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Feasibility of Hot Melt Extrusion in Converting Water-Based Nanosuspensions into Solid Dosage Forms.Pharmaceutics. 2025 May 17;17(5):662. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17050662. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40430953 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the Lower Critical Solution Temperature of Thermoresponsive Poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) Utilizing Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Monomers.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Mar 23;15(7):1595. doi: 10.3390/polym15071595. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37050207 Free PMC article.
-
4D printing: innovative solutions and technological advances in orthopedic repair and reconstruction, personalized treatment and drug delivery.Biomed Eng Online. 2025 Jan 21;24(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12938-025-01334-3. Biomed Eng Online. 2025. PMID: 39838448 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gupta R., Tripathi P., Bhardwaj P., Maho A. Recent advances in gastro retentive drug delivery systems and its application on treatment of H. Pylori infections. J. Anal. Pharm. Res. 2018;7:404–410. doi: 10.15406/japlr.2018.07.00258. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

