Deferasirox Nanosuspension Loaded Dissolving Microneedles for Intradermal Delivery
- PMID: 36559310
- PMCID: PMC9784557
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122817
Deferasirox Nanosuspension Loaded Dissolving Microneedles for Intradermal Delivery
Abstract
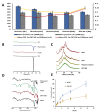
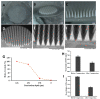
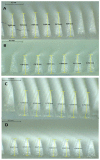
Microneedles are minimally invasive systems that can deliver drugs intradermally without pain and bleeding and can advantageously replace the hypodermal needles and oral routes of delivery. Deferasirox (DFS) is an iron chelator employed in several ailments where iron overload plays an important role in disease manifestation. In this study, DFS was formulated into a nanosuspension (NSs) through wet media milling employing PVA as a stabilizer and successfully loaded in polymeric dissolving microneedles (DMNs). The release studies for DFS-NS clearly showed a threefold increased dissolution rate compared to pure DFS. The mechanical characterization of DFS-NS-DMNs revealed that the system was sufficiently strong for efficacious skin penetration. Optical coherence tomography images confirmed an insertion of up to 378 µm into full-thickness porcine skin layers. The skin deposition studies showed 60% drug deposition from NS-DMN, which was much higher than from the DFS-NS transdermal patch (DFS-NS-TP) (without needles) or pure DFS-DMNs. Moreover, DFS-NS without DMNs did not deposit well inside the skin, indicating that DMNs played an important role in effectively delivering drugs inside the skin. Therefore, it is evident from the findings that loading DFS-NS into novel DMN devices can effectively deliver DFS transdermally.
Keywords: deferasirox; dissolving microneedles; intradermal delivery; nanocrystals; nanosuspension.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Deferasirox nanosuspension loaded dissolving microneedles for ocular drug delivery.Int J Pharm. 2024 Oct 25;664:124614. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.124614. Epub 2024 Aug 20. Int J Pharm. 2024. PMID: 39168286
-
Nestorone nanosuspension-loaded dissolving microneedles array patch: A promising novel approach for "on-demand" hormonal female-controlled peritcoital contraception.Int J Pharm. 2022 Feb 25;614:121422. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.121422. Epub 2021 Dec 25. Int J Pharm. 2022. PMID: 34958899
-
Nanosuspension-Loaded Dissolving Microneedle Patches for Enhanced Transdermal Delivery of a Highly Lipophilic Cannabidiol.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 May 7;19:4061-4079. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S452207. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38736651 Free PMC article.
-
Dissolving microneedles for brain delivery: Recent advances and challenges.Drug Discov Today. 2025 Apr;30(4):104330. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2025.104330. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Drug Discov Today. 2025. PMID: 40086788 Review.
-
Dissolving microneedles for melanoma: Most recent updates, challenges, and future perspectives.Int J Pharm. 2025 Mar 30;673:125382. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2025.125382. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Int J Pharm. 2025. PMID: 39988214 Review.
Cited by
-
Skin Vaccination with Ebola Virus Glycoprotein Using a Polyphosphazene-Based Microneedle Patch Protects Mice against Lethal Challenge.J Funct Biomater. 2022 Dec 27;14(1):16. doi: 10.3390/jfb14010016. J Funct Biomater. 2022. PMID: 36662063 Free PMC article.
-
Bimodal Dissolving Microneedles with Nanoparticle Coating and Encapsulation for Extended Dual-Drug Delivery.Small. 2025 Jul;21(30):e2502904. doi: 10.1002/smll.202502904. Epub 2025 May 26. Small. 2025. PMID: 40417960 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Combined Dry Powder Inhaler Comprising Nanosized Ketoprofen-Embedded Mannitol-Coated Microparticles for Pulmonary Inflammations: Development, In Vitro-In Silico Characterization, and Cell Line Evaluation.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jan 7;17(1):75. doi: 10.3390/ph17010075. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38256908 Free PMC article.
-
Calcipotriol Nanosuspension-Loaded Trilayer Dissolving Microneedle Patches for the Treatment of Psoriasis: In Vitro Delivery and In Vivo Antipsoriatic Activity Studies.Mol Pharm. 2024 Jun 3;21(6):2813-2827. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.3c01223. Epub 2024 May 16. Mol Pharm. 2024. PMID: 38752564 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Trends and Translational Challenges in Drug and Vaccine Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jan 11;16(1):98. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16010098. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38258108 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yadav P.R., Munni M.N., Campbell L., Mostofa G., Dobson L., Shittu M., Pattanayek S.K., Uddin M.J., Das D.B. Translation of Polymeric Microneedles for Treatment of Human Diseases: Recent Trends, Progress, and Challenges. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13:1132. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13081132. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Volpe-Zanutto F., Ferreira L.T., Permana A.D., Kirkby M., Paredes A.J., Vora L.K., Bonfanti A.P., Charlie-Silva I., Raposo C., Figueiredo M.C., et al. Artemether and Lumefantrine Dissolving Microneedle Patches with Improved Pharmacokinetic Performance and Antimalarial Efficacy in Mice Infected with Plasmodium Yoelii. J. Control. Release. 2021;333:298–315. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.03.036. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vora L.K., Donnelly R.F., Larrañeta E., González-Vázquez P., Thakur R.R.S., Vavia P.R. Novel Bilayer Dissolving Microneedle Arrays with Concentrated PLGA Nano-Microparticles for Targeted Intradermal Delivery: Proof of Concept. J. Control. Release. 2017;265:93–101. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.10.005. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

