Improved Topical Drug Delivery: Role of Permeation Enhancers and Advanced Approaches
- PMID: 36559311
- PMCID: PMC9785322
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122818
Improved Topical Drug Delivery: Role of Permeation Enhancers and Advanced Approaches
Abstract
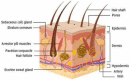
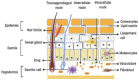
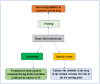
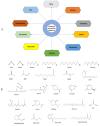
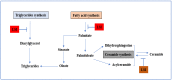
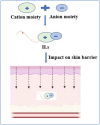
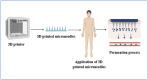
The delivery of drugs via transdermal routes is an attractive approach due to ease of administration, bypassing of the first-pass metabolism, and the large skin surface area. However, a major drawback is an inability to surmount the skin's stratum corneum (SC) layer. Therefore, techniques reversibly modifying the stratum corneum have been a classical approach. Surmounting the significant barrier properties of the skin in a well-organised, momentary, and harmless approach is still challenging. Chemical permeation enhancers (CPEs) with higher activity are associated with certain side effects restricting their advancement in transdermal drug delivery. Furthermore, complexity in the interaction of CPEs with the skin has led to difficulty in elucidating the mechanism of action. Nevertheless, CPEs-aided transdermal drug delivery will accomplish its full potential due to advancements in analytical techniques, synthetic chemistry, and combinatorial studies. This review focused on techniques such as drug-vehicle interaction, vesicles and their analogues, and novel CPEs such as lipid synthesis inhibitors (LSIs), cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs), and ionic liquids (ILs). In addition, different types of microneedles, including 3D-printed microneedles, have been focused on in this review.
Keywords: cell penetration peptides; drug delivery; ionic liquids; microneedle; permeation enhancers; stratum corneum; transdermal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Schaefer H., Redelmeier T.E. Skin Barrier. Karger Publishers; Basel, Switzerland: 1996.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

