Genome Size in the Arenaria ciliata Species Complex (Caryophyllaceae), with Special Focus on A. ciliata subsp. bernensis, a Narrow Endemic of the Swiss Northern Alps
- PMID: 36559611
- PMCID: PMC9783149
- DOI: 10.3390/plants11243489
Genome Size in the Arenaria ciliata Species Complex (Caryophyllaceae), with Special Focus on A. ciliata subsp. bernensis, a Narrow Endemic of the Swiss Northern Alps
Abstract
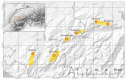
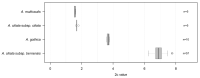
The genus Arenaria (Caryophyllaceae) comprises approximately 300 species worldwide; however, to date, just six of these taxa have been investigated in terms of their genome size. The main subject of the present study is the A. ciliata species complex, with special focus on A. ciliata subsp. bernensis, an endemic plant occurring in the Swiss Northern Alps. Altogether, 16 populations and 77 individuals of the A. ciliata complex have been sampled and their genome sizes were estimated using flow cytometry, including A. ciliata subsp. bernensis, A. ciliata s.str., A. multicaulis, and A. gothica. The Arenaria ciliata subsp. bernensis shows the highest 2c-value of 6.91 pg of DNA, while A. gothica showed 2c = 3.69 pg, A. ciliata s.str. 2c = 1.71 pg, and A. multicaulis 2c = 1.57 pg. These results confirm the very high ploidy level of A. ciliata subsp. bernensis (2n = 20x = 200) compared to other taxa in the complex, as detected by our chromosome counting and previously documented by earlier work. The genome size and, thus, also the ploidy level, is stable across the whole distribution area of this taxon. The present study delivers additional support for the taxonomic distinctiveness of the high alpine endemic A. ciliata subsp. bernensis, which strongly aligns with other differences in morphology, phylogeny, phenology, ecology, and plant communities, described previously. In affirming these differences, further support now exists to re-consider the species status of this taxon. Upgrading to full species rank would significantly improve the conservation prospects for this taxon, as, because of its precise ecological adaptation to alpine summit habitats, the A. ciliata subsp. bernensis faces acute threats from accelerated climate warming.
Keywords: arctic-alpine plants; disjunctions; flow cytometry; narrow endemism; polyploidy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome Size in the Arenaria ciliata Species Complex (Caryophyllaceae), with Special Focus on Northern Europe and the Arctic.Plants (Basel). 2024 Feb 26;13(5):635. doi: 10.3390/plants13050635. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38475481 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Taxonomy of Armeria arenaria (Plumbaginaceae), with a Special Focus on the Putative Subspecies Endemic to the Apennines.Biology (Basel). 2022 Jul 14;11(7):1060. doi: 10.3390/biology11071060. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36101438 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Size, Chromosome Number and Morphological Data Reveal Unexpected Infraspecific Variability in Festuca (Poaceae).Genes (Basel). 2021 Jun 11;12(6):906. doi: 10.3390/genes12060906. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34208200 Free PMC article.
-
A glacial survivor of the alpine Mediterranean region: phylogenetic and phylogeographic insights into Silene ciliata Pourr. (Caryophyllaceae).PeerJ. 2015 Aug 20;3:e1193. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1193. eCollection 2015. PeerJ. 2015. PMID: 26312184 Free PMC article.
-
Polyploidisation and geographic differentiation drive diversification in a European High Mountain Plant Group (Doronicum clusii Aggregate, Asteraceae).PLoS One. 2015 Mar 6;10(3):e0118197. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118197. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25749621 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Understanding Arctic-Alpine Plants from Ecological and Evolutionary Perspectives.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jun 5;13(11):1560. doi: 10.3390/plants13111560. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38891368 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Size in the Arenaria ciliata Species Complex (Caryophyllaceae), with Special Focus on Northern Europe and the Arctic.Plants (Basel). 2024 Feb 26;13(5):635. doi: 10.3390/plants13050635. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38475481 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bourge M., Brown S.C., Siljak-Yakovlev S. Flow cytometry as tool in plant sciences, with emphasis on genome size and ploidy level assessment. Genet. Applic. 2018;2:1–12. doi: 10.31383/ga.vol2iss2pp1-12. - DOI
-
- García-Fernández A., Iriondo J.M., Vallès J., Orellana J., Escidero A. Ploidy level and genome size of locally adapted populations of Silene ciliata across an altitudinal gradient. Plant Syst. Evol. 2012;298:139–146. doi: 10.1007/s00606-011-0530-3. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

