Induction of Male Sterility by Targeted Mutation of a Restorer-of-Fertility Gene with CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Genome Editing in Brassica napus L
- PMID: 36559613
- PMCID: PMC9785856
- DOI: 10.3390/plants11243501
Induction of Male Sterility by Targeted Mutation of a Restorer-of-Fertility Gene with CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Genome Editing in Brassica napus L
Abstract
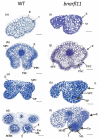
Brassica napus L. (canola, oil seed rape) is one of the world's most important oil seed crops. In the last four decades, the discovery of cytoplasmic male-sterility (CMS) systems and the restoration of fertility (Rf) genes in B. napus has improved the crop traits by heterosis. The homologs of Rf genes, known as the restoration of fertility-like (RFL) genes, have also gained importance because of their similarities with Rf genes. Such as a high non-synonymous/synonymous codon replacement ratio (dN/dS), autonomous gene duplications, and a possible engrossment in fertility restoration. B. napus contains 53 RFL genes on chromosomes A9 and C8. Our research aims to study the function of BnaRFL11 in fertility restoration using the CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing technique. A total of 88/108 (81.48%) T0 lines, and for T1, 110/145 (75%) lines carried T-DNA insertions. Stable mutations were detected in the T0 and T1 generations, with an average allelic mutation transmission rate of 81%. We used CRISPR-P software to detect off-target 50 plants sequenced from the T0 generation that showed no off-target mutation, signifying that if the designed sgRNA is specific for the target, the off-target effects are negligible. We also concluded that the mutagenic competence of the designed sgRNAs mediated by U6-26 and U6-29 ranged widely from 31% to 96%. The phenotypic analysis of bnarfl11 revealed defects in the floral structure, leaf size, branch number, and seed production. We discovered a significant difference between the sterile line and fertile line flower development after using a stereomicroscope and scanning electron microscope. The pollen visibility test showed that the pollen grain had utterly degenerated. The cytological observations of homozygous mutant plants showed an anther abortion stage similar to nap-CMS, with a Orf222, Orf139, Ap3, and nad5c gene upregulation. The bnarfl11 shows vegetative defects, including fewer branches and a reduced leaf size, suggesting that PPR-encoding genes are essential for the plants' vegetative and reproductive growth. Our results demonstrated that BnaRFL11 has a possible role in fertility restoration. The current study's findings suggest that CRISPR/Cas9 mutations may divulge the functions of genes in polyploid species and provide agronomically desirable traits through a targeted mutation.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; Rf-like (RFL); cytological study; genome editing; rapeseed CMS; sgRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures










References
-
- Van de Wouw A.P., Idnurm A., Davidson J.A., Sprague S.J., Khangura R.K., Ware A.H., Lindbeck K.D., Marcroft S.J. Fungal diseases of canola in Australia: Identification of trends, threats and potential therapies. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2016;45:415–423. doi: 10.1007/s13313-016-0428-1. - DOI
-
- Yang L.Y., Liu P.W., Yang G.S. Development of Polima temperature-sensitive cytoplasmic male sterile lines of Brassica napus through isolated microspore culture. Plant Breed. 2010;125:368–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0523.2006.01249.x. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

