Interaction of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid and Ca2+ on Phenolic Compounds Bioaccumulation in Soybean Sprouts under NaCl Stress
- PMID: 36559615
- PMCID: PMC9787623
- DOI: 10.3390/plants11243503
Interaction of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid and Ca2+ on Phenolic Compounds Bioaccumulation in Soybean Sprouts under NaCl Stress
Abstract
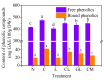
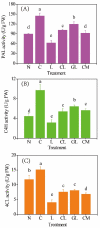
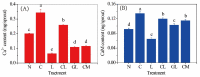
NaCl stress can enhance the accumulation of phenolic compounds in soybean during germination. In the present study, effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and Ca2+ on the biosynthesis of phenolic compounds in soybean sprouts germinated with NaCl stress were investigated. Results showed that addition of Ca2+ increased the content of total phenolics, phenolic acids, and isoflavonoids in soybean sprouts by ca. 15%, 7%, and 48%, respectively, through enhancing the activities of three key enzymes involved in the biosynthesis. On the other hand, addition of LaCl3, a calcium channel blocker, inhibited the synthesis of phenolic compounds, indicating that Ca2+ plays an important role in the synthesis of these compounds in soybean sprouts. Addition of GABA can increase the content of Ca2+ in soybean sprouts by ca. 20% and alleviate the inhibition of LaCl3 on phenolics biosynthesis in soybean sprouts. Similarly, addition of Ca2+ can reverse the inhibition of 3-mercaptopropionate, an inhibitor of endogenous GABA synthesis, on the biosynthesis of phenolic compounds in soybean sprouts under NaCl stress. To conclude, both GABA and Ca2+ can enhance the biosynthesis of phenolic compounds in soybean sprouts and there was an interaction between their effects on the promotion of phenolic compounds biosynthesis.
Keywords: Ca2+; GABA; NaCl stress; phenolic compounds; soybean sprout.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rady M.M., Boriek S.H.K., Abd El-Mageed T.A., Seif El-Yazal M.A., Ali E.F., Hassan F.A.S., Abdelkhalik A. Exogenous gibberellic acid or dilute bee honey boosts drought stress tolerance in vicia faba by rebalancing osmoprotectants, antioxidants, nutrients, and phytohormones. Plants. 2021;10:748. doi: 10.3390/plants10040748. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Houneida A., Hatem A., Khalid A., Esmat F.A., Hassan F.A.S., Samir A.E., Kamel H. Induced anti-oxidation efficiency and others by salt stress in Rosa damascena Miller. Sci. Hortic. 2020;274:109681.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

