Evaluation of Chemical Composition, Sun Protection Factor and Antioxidant Activity of Lithuanian Propolis and Its Plant Precursors
- PMID: 36559670
- PMCID: PMC9781500
- DOI: 10.3390/plants11243558
Evaluation of Chemical Composition, Sun Protection Factor and Antioxidant Activity of Lithuanian Propolis and Its Plant Precursors
Abstract
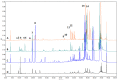
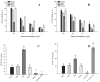
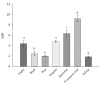
The growing interest in polyphenols of natural origin and their plant sources encourages the study of their chemical composition and biological activity. Propolis is widely used as a source of phenolic compounds. The aim of this study is to evaluate and compare the chemical composition, antioxidant activity and sun protection factor (SPF) of the ethanolic extracts of the poplar buds, birch buds and pine buds of propolis plant precursors collected in Lithuania. The IC50 concentration of the extracts was evaluated using DPPH and ABTS methods. Extracts of poplar buds, birch buds and propolis showed a lower IC50 concentration by ABTS and DPPH methods compared with pine buds extracts. Poplar buds and propolis extracts showed the highest SPF value, while birch and pine buds extracts showed a lower SPF value. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis results showed that phenolic acids, such as p-coumaric acid and cinnamic acid, and flavonoids, such as pinobanksin and pinocembrin, were identified in all the tested extracts. Salicin has been identified only in poplar buds extracts. The results of antioxidant activity showed that propolis poplar and birch buds are a promising source of biologically active polyphenols.
Keywords: UV protection; antioxidant activity; birch; extract; pine; poplar; propolis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extracts of Poplar Buds (Populus balsamifera L., Populus nigra L.) and Lithuanian Propolis: Comparison of Their Composition and Biological Activities.Plants (Basel). 2021 Apr 21;10(5):828. doi: 10.3390/plants10050828. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33919265 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Ethanolic and Aqueous Populus balsamifera L. Bud Extracts by Different Extraction Methods: Chemical Composition, Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Oct 2;14(10):1018. doi: 10.3390/ph14101018. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34681242 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Plant Origin on Eurasian Propolis on Phenolic Profile and Classical Antioxidant Activity.Biomolecules. 2021 Jan 6;11(1):68. doi: 10.3390/biom11010068. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33419208 Free PMC article.
-
Plant Sources Responsible for the Chemical Composition and Main Bioactive Properties of Poplar-Type Propolis.Plants (Basel). 2020 Dec 24;10(1):22. doi: 10.3390/plants10010022. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33374275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Composition and functional properties of propolis (bee glue): A review.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2019 Nov;26(7):1695-1703. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2018.08.013. Epub 2018 Aug 17. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31762646 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Application of Poloxamer for In Situ Eye Drop Modeling by Enrichment with Propolis and Balsam Poplar Buds Phenolic Compounds.Gels. 2024 Feb 21;10(3):161. doi: 10.3390/gels10030161. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38534579 Free PMC article.
-
The Comparative Study of the Antioxidant and Antibacterial Effects of Propolis Extracts in Veterinary Medicine.Vet Sci. 2024 Aug 15;11(8):375. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11080375. Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39195829 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical profiling, bioactive compounds, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities of Indonesian propolis extract produced by Tetragonula laeviceps.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 30;10(19):e38736. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38736. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39397935 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Benefits of Antioxidant Phytochemicals in Type 2 Diabetes.Molecules. 2023 Oct 21;28(20):7209. doi: 10.3390/molecules28207209. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37894687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Para-Hydroxycinnamic Acid Mitigates Senescence and Inflammaging in Human Skin Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 26;25(15):8153. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158153. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125721 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beserra F.P., Gushiken L.F.S., Hussni M.F., Ribeiro V.P., Bonamin F., Jackson C.J., Pellizzon C.H., Bastos J.K. Artepillin C as an Outstanding Phenolic Compound of Brazilian Green Propolis for Disease Treatment: A Review on Pharmacological Aspects. Phytother. Res. 2021;35:2274–2286. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6875. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rasouli H., Farzaei M.H., Khodarahmi R. Polyphenols and Their Benefits: A Review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017;20((Suppl. S2)):1700–1741. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2017.1354017. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

