Advances in Polymeric Colloids for Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 36559812
- PMCID: PMC9788371
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14245445
Advances in Polymeric Colloids for Cancer Treatment
Abstract
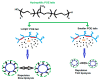
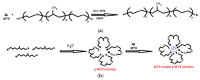
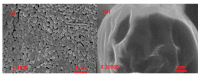
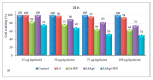
Polymer colloids have remarkable features and are gaining importance in many areas of research including medicinal science. Presently, the innovation of cancer drugs is at the top in the world. Polymer colloids have been used as drug delivery and diagnosis agents in cancer treatment. The polymer colloids may be of different types such as micelles, liposomes, emulsions, cationic carriers, and hydrogels. The current article describes the state-of-the-art polymer colloids for the treatment of cancer. The contents of this article are about the role of polymeric nanomaterials with special emphasis on the different types of colloidal materials and their applications in targeted cancer therapy including cancer diagnoses. In addition, attempts are made to discuss future perspectives. This article will be useful for academics, researchers, and regulatory authorities.
Keywords: cancer diagnosis and treatment; colloidal polymeric nanomaterials; future perspectives; polymer colloids.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest in this manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Polymeric micelles - a new generation of colloidal drug carriers.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 1999 Sep;48(2):101-11. doi: 10.1016/s0939-6411(99)00039-9. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 1999. PMID: 10469928 Review.
-
Chitosan hydrogels incorporating colloids for sustained drug delivery.Carbohydr Polym. 2022 Jan 1;275:118689. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118689. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Carbohydr Polym. 2022. PMID: 34742416 Review.
-
Polymer colloids as drug delivery systems for the treatment of arthritis.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2020 Nov;285:102273. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2020.102273. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2020. PMID: 33002783 Review.
-
Thermoresponsive polymer colloids for drug delivery and cancer therapy.Macromol Biosci. 2011 Dec 8;11(12):1722-34. doi: 10.1002/mabi.201100252. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Macromol Biosci. 2011. PMID: 22012834 Review.
-
Polymer-Based Nanomaterials and Applications for Vaccines and Drugs.Polymers (Basel). 2018 Jan 2;10(1):31. doi: 10.3390/polym10010031. Polymers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30966075 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Type-A Gelatin-Based Hydrogel Infiltration and Degradation in Titanium Foams as a Potential Method for Localised Drug Delivery.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Jan 5;15(2):275. doi: 10.3390/polym15020275. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36679157 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Nanoparticle Development for Drug Delivery: A Comprehensive Review of Polycaprolactone-Based Multi-Arm Architectures.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Apr 10;15(8):1835. doi: 10.3390/polym15081835. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37111982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel avenue in the successful synthesis of Schiff base macromolecules via innovative plasma and classical approaches.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 29;15(1):10840. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-94665-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40155415 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mahbub A.A., Aslam A., Elzubier M.E., El-Boshy M., Abdelghany A.H., Ahmad J., Idris S., Almaimani R., Alsaegh A., El-Readi Z., et al. Enhanced anti-cancer effects of oestrogen and progesterone co-therapy against colorectal cancer in males. Front. Endocrinol. 2022;13:941834. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.941834. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Idris S., Refaat B., Almaimani R.A., Ahmed H.G., Ahmad J., Alhadrami M., El-Readi M.Z., Elzubier M.E., Alaufi H.A.A., Al-Amin B., et al. Enhanced in vitro tumoricidal effects of 5-Fluorouracil, thymoquinone, and active vitamin D3 triple therapy against colon cancer cells by attenuating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Life Sci. 2022;296:120442. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120442. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sharhan N.A.A., Messaoudi S.A., Babu S.R., Chaudhary A.R.B., Alsharm A.A., Alrefaei A.F., Kadasah S., Abu-Elmagd M., Assidi M., Buhmeida A., et al. Utility of Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Assessing Microsatellite Instability and Loss of Heterozygosity in Breast Cancer Using Human Identification Approach. Genes. 2022;13:590. doi: 10.3390/genes13040590. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

