Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate- co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (P(3HB- co-3HV))/Bacterial Cellulose (BC) Biocomposites for Potential Use in Biomedical Applications
- PMID: 36559911
- PMCID: PMC9786213
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14245544
Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate- co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (P(3HB- co-3HV))/Bacterial Cellulose (BC) Biocomposites for Potential Use in Biomedical Applications
Abstract
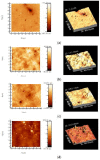
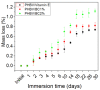
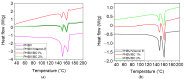
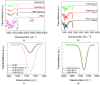
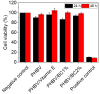
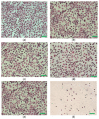
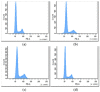
The aim of this study was to obtain biocomposites consisting of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV), bacterial cellulose (BC) and α-tocopherol by a melt processing technique for potential use in biomedical applications. The melt processing and roughness of biocomposites were evaluated and compared to sample without BC. The degradation rate of PHBV/BC biocomposites was measured in phosphate buffer saline (PBS) by determining the mass variation and evidencing of thermal and structural changes by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and attenuated total reflectance-Fourier transformed infrared spectrometry (ATR-FTIR). The cell viability, cell morphology, cell cycle distribution and total collagen content were investigated on murine NCTC fibroblasts. Overall, the adding of BC to polyester matrix led to an adequate melt processing of biocomposites and increased surface roughness and cytocompatibility, allowing the cells to secrete the extracellular matrix (collagen) and stimulate cell proliferation. Results showed that the PHBV/BC biocomposites were favorable for long-term degradation and could be used for the design of medical devices with controlled degradability.
Keywords: bacterial cellulose; biocomposite; crystallinity; in vitro cytocompatibility; melt processing; poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-valerate).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Accelerated Weathering Testing (AWT) and Bacterial Biodegradation Effects on Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV)/Rapeseed Microfiber Biocomposites Properties.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Feb 24;16(5):622. doi: 10.3390/polym16050622. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38475304 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) biocomposites with reinforcement by hydroxyapatite using extrusion processing.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016 Aug 1;65:19-26. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2016.04.024. Epub 2016 Apr 9. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016. PMID: 27157723
-
Thermal and Mechanical Properties of the Biocomposites of Miscanthus Biocarbon and Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-co-3-Hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV).Polymers (Basel). 2020 Jun 6;12(6):1300. doi: 10.3390/polym12061300. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32517200 Free PMC article.
-
Comonomer compositional distribution and thermal and morphological characteristics of bacterial poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)s with high 3-hydroxyvalerate content.Biomacromolecules. 2001 Winter;2(4):1315-23. doi: 10.1021/bm010128o. Biomacromolecules. 2001. PMID: 11777409
-
Oxygen Barrier and Thermomechanical Properties of Poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Biocomposites Reinforced with Calcium Carbonate Particles.Acta Chim Slov. 2020 Mar;67(1):137-150. Acta Chim Slov. 2020. PMID: 33558918
Cited by
-
Self-Reinforced Biocomposites Made from Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV): An Innovative Approach to Sustainable Packaging Production through Melt Processing.ACS Omega. 2024 Dec 17;9(52):51073-51088. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c05957. eCollection 2024 Dec 31. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39758632 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive and Physico-Chemical Assessment of Innovative Poly(lactic acid)-Based Biocomposites Containing Sage, Coconut Oil, and Modified Nanoclay.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 11;24(4):3646. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043646. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835080 Free PMC article.
-
Bioconversion of food waste to poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) biopolymer using Stenotrophomonas geniculata: study of operating parameters and process optimization.Biodegradation. 2025 Jul 5;36(4):57. doi: 10.1007/s10532-025-10156-y. Biodegradation. 2025. PMID: 40616686
-
Biomedical Applications of the Biopolymer Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV): Drug Encapsulation and Scaffold Fabrication.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 19;24(14):11674. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411674. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Bioelectrochemical Strategies for Enhanced Polyhydroxyalkanoate Production.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Jun 5;12(6):616. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12060616. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40564432 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ciesielski S., Mozejko J., Pisutpaisal N. Plant oils as promising substrates for polyhydroxyalkanoates production. J. Clean. Prod. 2015;106:408–421. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.09.040. - DOI
-
- Yao C.L., Chen J.H., Lee C.H. Effects of various monomers and micro-structure of polyhydroxyalkanoates on the behavior of endothelial progenitor cells and endothelial cells for vascular tissue engineering. J. Polym. Res. 2017;25:187. doi: 10.1007/s10965-017-1341-1. - DOI
-
- Panith N., Assavanig A., Lertsiri S., Bergkvist M., Surarit R., Niamsiri N. Development of tunable biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoates microspheres for controlled delivery of tetracycline for treating periodontal disease. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016;133:44128–44140. doi: 10.1002/app.44128. - DOI
-
- da Silva T.G., Gobbi V.G., Teixeira B.N., Mendonca T.D., Cubica T.B., Aquino L.F., Silva J.A.D., Thire R., Mendonca R.H. Mass Variation Rate, in Acidic Environment, of Polyhydroxybutyrate and Chitosan matrices with Potential Application as Controlled Drug Delivery System. Mater. Res.-Ibero-Am. J. Mater. 2019;22:e20180863. doi: 10.1590/1980-5373-mr-2018-0863. - DOI
Grants and funding
- PN-III-P3-3.5-EUK-2019-0237, Contract no. 219/23.12.2020 (NonActivPans)/Ministerul Cercetării și Inovării
- National Programme Nucleu, project no. 25N/2019-19270102 (3D-BIOMAT)/Ministerul Cercetării și Inovării
- PNII-Partnerships in Priority Areas, Contract no. 158/2012 (Polybac)/Ministerul Cercetării și Inovării
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

