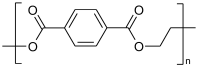
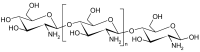
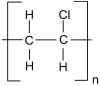
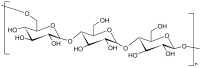
Chemical Structures, Properties, and Applications of Selected Crude Oil-Based and Bio-Based Polymers
- PMID: 36559918
- PMCID: PMC9783367
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14245551
Chemical Structures, Properties, and Applications of Selected Crude Oil-Based and Bio-Based Polymers
Abstract
The growing perspective of running out of crude oil followed by increasing prices for all crude oil-based materials, e.g., crude oil-based polymers, which have a huge number of practical applications but are usually neither biodegradable nor environmentally friendly, has resulted in searching for their substitutes-namely, bio-based polymers. Currently, both these types of polymers are used in practice worldwide. Owing to the advantages and disadvantages occurring among plastics with different origin, in this current review data on selected popular crude oil-based and bio-based polymers has been collected in order to compare their practical applications resulting from their composition, chemical structure, and related physical and chemical properties. The main goal is to compare polymers in pairs, which have the same or similar practical applications, regardless of different origin and composition. It has been proven that many crude oil-based polymers can be effectively replaced by bio-based polymers without significant loss of properties that ensure practical applications. Additionally, biopolymers have higher potential than crude oil-based polymers in many modern applications. It is concluded that the future of polymers will belong to bio-based rather than crude oil-based polymers.
Keywords: application; bio-based polymers; chemical structure; crude oil-based; properties.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Planning Implications Related to Sterilization-Sensitive Science Investigations Associated with Mars Sample Return (MSR).Astrobiology. 2022 Jun;22(S1):S112-S164. doi: 10.1089/AST.2021.0113. Epub 2022 May 19. Astrobiology. 2022. PMID: 34904892
-
Review on Spinning of Biopolymer Fibers from Starch.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Apr 1;13(7):1121. doi: 10.3390/polym13071121. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33915955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmentally Friendly Strategies for Formulating Vegetable Oil-Based Nanoparticles for Anticancer Medicine.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jul 8;15(7):1908. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071908. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37514094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bio-Polyethylene (Bio-PE), Bio-Polypropylene (Bio-PP) and Bio-Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (Bio-PET): Recent Developments in Bio-Based Polymers Analogous to Petroleum-Derived Ones for Packaging and Engineering Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2020 Jul 23;12(8):1641. doi: 10.3390/polym12081641. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32718011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanical, chemical, and bio-recycling of biodegradable plastics: A review.Sci Total Environ. 2023 Jul 15;882:163446. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.163446. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Sci Total Environ. 2023. PMID: 37075991 Review.
References
-
- Bhunia H.P., Basak A., Chaki T.K., Nando G.B. Synthesis and characterization of polymers from cashew nut shell liquid: A renewable resource V. Synthesis of copolyester. Eur. Polym. J. 2000;36:1157–1165. doi: 10.1016/S0014-3057(99)00171-8. - DOI
-
- Clark J.H. Green chemistry: Today (and tomorrow) Green Chem. 2006;8:17–21. doi: 10.1039/B516637N. - DOI
-
- Scott G. “Green” polymers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2000;68:1–7. doi: 10.1016/S0141-3910(99)00182-2. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

