Real-Time Human Activity Recognition with IMU and Encoder Sensors in Wearable Exoskeleton Robot via Deep Learning Networks
- PMID: 36560059
- PMCID: PMC9783602
- DOI: 10.3390/s22249690
Real-Time Human Activity Recognition with IMU and Encoder Sensors in Wearable Exoskeleton Robot via Deep Learning Networks
Abstract
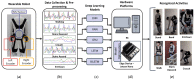
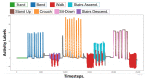
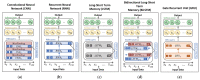
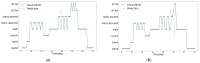
Wearable exoskeleton robots have become a promising technology for supporting human motions in multiple tasks. Activity recognition in real-time provides useful information to enhance the robot's control assistance for daily tasks. This work implements a real-time activity recognition system based on the activity signals of an inertial measurement unit (IMU) and a pair of rotary encoders integrated into the exoskeleton robot. Five deep learning models have been trained and evaluated for activity recognition. As a result, a subset of optimized deep learning models was transferred to an edge device for real-time evaluation in a continuous action environment using eight common human tasks: stand, bend, crouch, walk, sit-down, sit-up, and ascend and descend stairs. These eight robot wearer's activities are recognized with an average accuracy of 97.35% in real-time tests, with an inference time under 10 ms and an overall latency of 0.506 s per recognition using the selected edge device.
Keywords: deep learning networks; encoders; inertial measurement unit; real-time human activity recognition; wearable exoskeleton robot.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Huo W., Mohammed S., Moreno J.C., Amirat Y. Lower Limb Wearable Robots for Assistance and Rehabilitation: A State of the Art. IEEE Syst. J. 2016;10:1068–1081. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2014.2351491. - DOI
-
- Chen K., Zhang D., Yao L., Guo B., Yu Z., Liu Y. Deep Learning for Sensor-Based Human Activity Recognition: Overview, Challenges, and Opportunities. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021;54:77. doi: 10.1145/3447744. - DOI
-
- Kuschan J., Burgdorff M., Filaretov H., Krüger J. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. Volume 1140. IOP Publishing; Bristol, UK: 2021. Inertial Measurement Unit Based Human Action Recognition for Soft-Robotic Exoskeleton; p. 012020. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

