Predicting Vaccination Intention against COVID-19 Using Theory of Planned Behavior: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 36560436
- PMCID: PMC9783170
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines10122026
Predicting Vaccination Intention against COVID-19 Using Theory of Planned Behavior: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
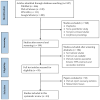
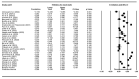
This study systematically analyzed the literature using the theory of planned behavior (TPB) as a theoretical framework to examine the influence of its constructs on vaccination intention against COVID-19. Quantitative studies were searched in PubMed, CINAHL, Web of Science, and Google Scholar following the PRISMA guidelines. The average rate of COVID-19 vaccination intention was 73.19%, ranging from 31% to 88.86%. Attitude had the strongest association with vaccination intention (r+ = 0.487, 95% CI: 0.368-0.590), followed by subjective norms (r+ = 0.409, 95% CI: 0.300-0.507), and perceived behavioral control (r+ = 0.286, 95% CI: 0.198-0.369). Subgroup analyses showed that the pooled effect sizes of TPB constructs on vaccination intention varied across geographic regions and study populations. Attitude had large effect sizes in Asia, Europe, and Oceania, especially among the adult general population, parents, and patients. Subjective norms had large effect sizes in Asia and Oceania, especially among parents and patients. Perceived behavioral control was the most dominant predictor of vaccination acceptance in Africa among patients. These findings suggest that TPB provides a useful framework for predicting intention to receive a COVID-19 vaccine. Hence, public awareness and educational programs aimed at promoting COVID-19 vaccination intention should consider using TPB as a framework to achieve the goal.
Keywords: COVID-19; attitude; meta-analysis; perceived behavioral control; subjective norms; systematic review; theory of planned behavior; vaccination intention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19. 11 March 2020. [(accessed on 30 December 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-genera....
-
- World Health Organization WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 25 September 2022)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- World Health Organization DRAFT Landscape of COVID-19 Candidate Vaccine. 22 January. 2021. [(accessed on 22 January 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/draft-landscape-of-covid-19-cand....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

