mRNA-Based Vaccines and Therapeutics for COVID-19 and Future Pandemics
- PMID: 36560560
- PMCID: PMC9785933
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines10122150
mRNA-Based Vaccines and Therapeutics for COVID-19 and Future Pandemics
Abstract
An unheard mobilization of resources to find SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and therapies has been sparked by the COVID-19 pandemic. Two years ago, COVID-19's launch propelled mRNA-based technologies into the public eye. Knowledge gained from mRNA technology used to combat COVID-19 is assisting in the creation of treatments and vaccines to treat existing illnesses and may avert pandemics in the future. Exploiting the capacity of mRNA to create therapeutic proteins to impede or treat a variety of illnesses, including cancer, is the main goal of the quickly developing, highly multidisciplinary field of biomedicine. In this review, we explore the potential of mRNA as a vaccine and therapeutic using current research findings.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; mRNA vaccine; pandemic; therapeutics; virus outbreak.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


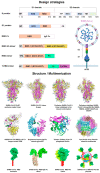
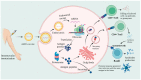
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

