Immune Response to Third and Fourth COVID-19 Vaccination in Hemodialysis Patients and Kidney Transplant Recipients
- PMID: 36560648
- PMCID: PMC9785871
- DOI: 10.3390/v14122646
Immune Response to Third and Fourth COVID-19 Vaccination in Hemodialysis Patients and Kidney Transplant Recipients
Abstract
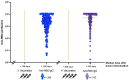
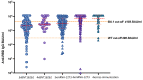
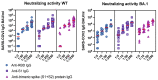
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a serious hazard for hemodialysis (HD) patients and kidney transplant (KTX) recipients as they suffer from an impaired immune response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. In addition, a definition of SARS-CoV-2 IgG titer that indicates a sufficient immune response, especially against new omicron variants, is urgently needed. In the present study, the immune response to either a third or a fourth dose of a mRNA vaccine was investigated in 309 dialysis and 36 KTX patients. SARS-CoV-2 IgG titer thresholds indicating neutralizing activity against wild type (WT) and the omicron variant BA.1 were quantified. After four vaccine doses, a high-neutralizing activity against WT was evidenced in HD patients, whereas the neutralizing rate against BA.1 was significant lower. Concerning KTX recipients, humoral and cellular immune responses after a third vaccination were still highly impaired. This calls for modified omicron-targeting vaccines.
Keywords: BA.1; SARS-CoV-2; booster; dialysis; immunosuppression; kidney disease; neutralization; protection; surrogate; transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Espi M., Charmetant X., Barba T., Koppe L., Pelletier C., Kalbacher E., Chalencon E., Mathias V., Ovize A., Cart-Tanneur E., et al. The ROMANOV study found impaired humoral and cellular immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine in virus-unexposed patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2021;100:928–936. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2021.07.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alcázar-Arroyo R., Portolés J., López-Sánchez P., Zalamea F., Furaz K., Méndez Á., Nieto L., Sánchez-Hernández R., Pizarro S., García A., et al. Rapid decline of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in patients on haemodialysis: The COVID-FRIAT study. Clin. Kidney J. 2021;14:1835–1844. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfab048. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Affeldt P., Koehler F.C., Brensing K.A., Adam V., Burian J., Butt L., Gies M., Grundmann F., Hinrichs S., Johannis W., et al. Immune Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Vaccination in Dialysis Patients and Kidney Transplant Recipients. Microorganisms. 2021;10:4. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10010004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- De Vriese A.S., Van Praet J., Reynders M., Heylen L., Viaene L., Caluwé R., Schoutteten M., De Bacquer D. Longevity and correlation with disease severity of the humoral and cellular response to SARS-CoV-2 infection in haemodialysis patients. Clin. Kidney J. 2021;14:2446–2448. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfab147. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sakhi H., Dahmane D., Attias P., Kofman T., Bouvier M., Lapidus N., Fourati S., El Karoui K., Mondor NephroCov Study Group Kinetics of Anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgG Antibodies in Hemodialysis Patients Six Months after Infection. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021;32:1033–1036. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020111618. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

