RAD-140 Drug-Induced Liver Injury
- PMID: 36561105
- PMCID: PMC9753945
- DOI: 10.31486/toj.22.0005
RAD-140 Drug-Induced Liver Injury
Abstract
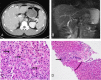
Background: RAD-140, one of the novel selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs), has potent anabolic effects on bones and muscles with little androgenic effect. Despite the lack of approval for its clinical use, RAD-140 is readily accessible on the consumer market. Hepatotoxicity associated with the use of SARMs has only rarely been reported in the literature. Case Report: A 24-year-old male presented with a 2-week history of diffuse abdominal pain, scleral icterus, pruritus, and jaundice. Prior to presentation, he had been taking the health supplement RAD-140 for muscle growth for 5 weeks. He had a cholestatic pattern of liver injury, with a peak total bilirubin of 38.5 mg/dL. Liver biopsy was supportive of a diagnosis of RAD-140-associated liver injury characterized pathologically by intracytoplasmic and canalicular cholestasis with minimal portal inflammation. Symptoms and liver injury resolved after cessation of the offending agent. Conclusion: To date, only select descriptions of the potential hepatoxicity associated with the use of SARMs, including RAD-140, have been published. Given their potential hepatoxicity and ready availability on the consumer market, RAD-140 and other SARMs should be used judiciously and under close clinical supervision until further hepatic safety data become available.
Keywords: Chemical and drug induced liver injury; Enobosarm; LGD-4033; RAD140.
©2022 by the author(s); Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY).
Figures
References
-
- FDA in brief: FDA warns against using SARMs in body building products. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Published October 31, 2017. Accessed March 8, 2022. fda.gov/news-events/fda-brief/fda-brief-fda-warns-against-using-sarms-bo...
-
- The prohibited list. World Anti-Doping Agency. Published January 1, 2022. Accessed March 8, 2022. wada-ama.org/en/prohibited-list
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
