Research progress on effects of traditional Chinese medicine on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: A review
- PMID: 36561346
- PMCID: PMC9763941
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1055248
Research progress on effects of traditional Chinese medicine on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: A review
Abstract
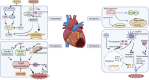
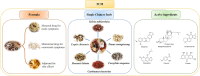
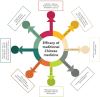
Ischemic heart disease (IHD) is a high-risk disease in the middle-aged and elderly population. The ischemic heart may be further damaged after reperfusion therapy with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and other methods, namely, myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (MIRI), which further affects revascularization and hinders patient rehabilitation. Therefore, the investigation of new therapies against MIRI has drawn great global attention. Within the long history of the prevention and treatment of MIRI, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has increasingly been recognized by the scientific community for its multi-component and multi-target effects. These multi-target effects provide a conspicuous advantage to the anti-MIRI of TCM to overcome the shortcomings of single-component drugs, thereby pointing toward a novel avenue for the treatment of MIRI. However, very few reviews have summarized the currently available anti-MIRI of TCM. Therefore, a systematic data mining of TCM for protecting against MIRI will certainly accelerate the processes of drug discovery and help to identify safe candidates with synergistic formulations. The present review aims to describe TCM-based research in MIRI treatment through electronic retrieval of articles, patents, and ethnopharmacology documents. This review reported the progress of research on the active ingredients, efficacy, and underlying mechanism of anti-MIRI in TCM and TCM formulas, provided scientific support to the clinical use of TCM in the treatment of MIRI, and revealed the corresponding clinical significance and development prospects of TCM in treating MIRI.
Keywords: cardioprotective effects; molecular mechanisms; myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury; pathogenesis; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2022 Xing, Long, Zhang, Fu, Huang, Chaurembo, Chanda, Xu, Shu, Lin, Yang and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antiplatelet Therapy with Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine for Use in Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: A Review of Clinical Applications and Mechanisms.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Jul 20;2021:7409094. doi: 10.1155/2021/7409094. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34335837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pathological mechanisms and potential therapeutic drugs for myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jul;129:155649. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155649. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38653154 Review.
-
[Regulation of myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury signal pathway by flavonoid monomer].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Feb;48(4):879-889. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220913.701. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 36872258 Chinese.
-
Targeting mitochondrial circadian rhythms: The potential intervention strategies of Traditional Chinese medicine for myocardial ischaemia‒reperfusion injury.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Oct;166:115432. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115432. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37673019 Review.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine formulas for the treatment of osteoporosis: Implication for antiosteoporotic drug discovery.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Aug 2;189:61-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.05.025. Epub 2016 May 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27180315 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of the SIRT3/SOD2 Signaling Pathway by a Compound Mixture from Polygonum orientale L. for Myocardial Damage.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Sep 27;17(10):1288. doi: 10.3390/ph17101288. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39458930 Free PMC article.
-
Taohong Siwu Decoction Combined With the LncRNA H19/miR-675-5p Axis Repairs Limb Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Through the Regulation of the Wnt3a/Ca2+ Signaling Pathway.Mediators Inflamm. 2025 Feb 23;2025:3096848. doi: 10.1155/mi/3096848. eCollection 2025. Mediators Inflamm. 2025. PMID: 40034562 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive evaluation of non-coding RNA-mediated autophagy regulation in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 25;16:1581341. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1581341. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40351430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety and efficacy evaluation of Simo decoction and Arecae semen in herbal medicine practice.Heliyon. 2024 May 16;10(11):e31373. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31373. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38841513 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon dots derived from Ligusticum Chuanxiong mitigate cardiac injury by disrupting the harmful oxidative stress-apoptosis cycle.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 May 29;23(1):391. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03477-w. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40442709 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bai X. J., Ren J. X. (2014). The treatment of No-reflow occurring during percutaneous coronary intervention on the pathogenesis of insidious phlegm. Chin. J. Exp. Traditional Med. Formulae 20 (16), 237–240. 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2014160237 - DOI
-
- Billah M. M., Khan F., Niaz K. (2019). Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. Nonvitamin Nonmineral Nutr. Suppl. 2019, 403–408. 10.1016/B978-0-12-812491-8.00054-0 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous