Great Toe Transplantation
- PMID: 36561428
- PMCID: PMC9762995
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0042-1758689
Great Toe Transplantation
Abstract
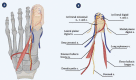
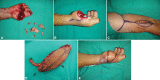
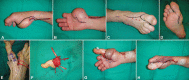
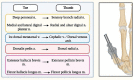
Despite being relatively uncommon in the general population, thumb amputations cause severe disability. More than 3,300 thumb amputations occurred in the United States. The thumb makes up around 40% of the function of the hand. Therefore, losing it would result in significant medical, hospital, and societal costs. Thumb reconstruction surgery's primary goal is to restore grip strength, including the range of motion, fine and tripod pinch, power grasp, strength, and sensibility, while secondary goals include restoring hand aesthetics. In cases of thumb replantation, like-for-like replacement is possible; however, when thumb replantation is not possible, great toe-to-hand transplantation is the best available reconstruction. When compared with other reconstructive options such as osteoplastic thumb reconstruction, pollicization, second toe transplantation, and the use of a thumb prosthesis, great toe transplantation provides superior function and aesthetics. For restoring pinch, sensitivity, strength, and aesthetics of the hand with well-tolerated donor site morbidity, toe to thumb transplantation is regarded as the gold standard.
Keywords: amputation; extremities; microsurgery; reconstructive surgical procedures; thumb; vascularized composite allotransplantation.
Thieme. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None declared.
Figures
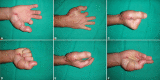

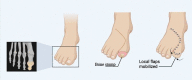
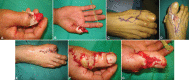
References
-
- Shale C M, Tidwell J E, III, Mulligan R P, Jupiter D C, Mahabir R C. A nationwide review of the treatment patterns of traumatic thumb amputations. Ann Plast Surg. 2013;70(06):647–651. - PubMed
-
- Engel J, Luboshitz S, Jaffe B, Rotstein Z. To trim or replant: a matter of cost. World J Surg. 1991;15(04):486–492. - PubMed
-
- Robinson L S, Sarkies M, Brown T, O'Brien L. Direct, indirect and intangible costs of acute hand and wrist injuries: a systematic review. Injury. 2016;47(12):2614–2626. - PubMed

