Diagnostic value of circulating lncRNAs for gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36561519
- PMCID: PMC9763557
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1058028
Diagnostic value of circulating lncRNAs for gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: With the prevalence of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology, a large number of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have attracted tremendous attention and have been the topic of extensive research on gastric cancer (GC). It was revealed that lncRNAs not only participate in the transduction of various signaling pathways, thus influencing GC genesis and development, but also have the potential for GC diagnosis. Therefore, we aimed to conduct a meta-analysis of previous studies on GC.
Materials and methods: An electronic search was made before August 2021 on databases including PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science. Relevant articles that compare lncRNA expression in GC patients and healthy controls were summarized. We conducted a meta-analysis with the objective of evaluating the ability of lncRNAs in diagnosing GC.
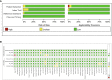
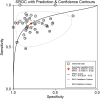
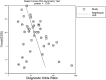
Results: A total of 40 original research studies including 6,772 participants were discussed in this meta-analysis. The overall sensitivity, specificity, and the area under the curve (AUC) were 0.78 (95% CI: 0.75-0.81), 0.79 (95% CI: 0.74-0.83), and 0.85 (95% CI: 0.81-0.87), respectively. The value of pooled diagnostic odds ratios (DORs) was 13.00 (95% CI: 10.00-17.00).
Conclusions: This meta-analysis revealed that serum or plasma lncRNAs have high sensitivity and specificity, which makes lncRNAs clinically feasible in diagnosing GC. The results from this meta-analysis demonstrated that peripheral blood lncRNAs may become novel noninvasive biomarkers in the foreseeable future. At the same time, it should be noted that a greater number of blood samples and more evidence from rigorous multicenter clinical studies are necessary to justify their applicability as cancer biomarkers.
Keywords: diagnosis; gastric cancer; lncRNA; meta - analysis; systematic review.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Zhang, Xu, Zhang, Bei, Ding, Zhang and Feng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

