Clinical and biochemical characteristics of people experiencing post-coronavirus disease 2019-related symptoms: A prospective follow-up investigation
- PMID: 36561720
- PMCID: PMC9763306
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1067082
Clinical and biochemical characteristics of people experiencing post-coronavirus disease 2019-related symptoms: A prospective follow-up investigation
Abstract
Background: Post-acute coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) syndrome, also known as long COVID, is a prolonged illness after the acute phase of COVID-19. Hospitalized patients were known to have persisting symptoms of fatigue, headache, dyspnea, and anosmia. There is a need to describe the characteristics of individuals with post-COVID-19 symptoms in comparison to the baseline characteristics.
Purpose: To investigate the clinical and biochemical characteristics of people who recovered from COVID-19 after 6 months of discharge from the hospital.
Methods: This was a prospective follow-up investigation of hospitalized and discharged COVID-19 patients. Adult patients admitted to King Saud University Medical City, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 and discharged were recruited. The baseline demographic information, comorbidities, vital signs and symptoms, laboratory parameters, COVID-19 therapy, and outcomes were collected from the medical records. Blood samples were collected for cytokines estimation. A detailed interview about signs and symptoms was undertaken during the follow-up.
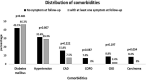
Results: Half of the followed-up people reported experiencing at least one of the COVID-19-related symptoms. The mean blood pressure was found higher in follow-up. People with the symptoms were characterized by low lymphocyte count, lower serum calcium levels, and hyperglycemia compared to people without any post-COVID-19 symptoms. Cytokines IL-8, VEGF, and MCP-1 were higher in people with the most frequent symptoms.
Conclusion: People with post-COVID-19 symptoms were characterized by lower lymphocyte count, lower serum calcium levels, and hyperglycemia compared to people without symptoms. Individuals with the most frequent post-COVID-19 symptoms had higher baseline pro-inflammatory, chemotactic, and angiogenic cytokines.
Keywords: COVID-19; PASC; SARS-CoV-2; long COVID; post-COVID-19.
Copyright © 2022 Alfadda, Rafiullah, Alkhowaiter, Alotaibi, Alzahrani, Binkhamis, Siddiqui, Youssef, Altalhi, Almaghlouth, Alarifi, Albanyan, Alosaimi, Isnani, Nawaz and Alayed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

