Right Heart Clot-in-Transit: Endovascular Therapies
- PMID: 36561934
- PMCID: PMC9767789
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0042-1757942
Right Heart Clot-in-Transit: Endovascular Therapies
Abstract
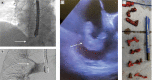
Right heart thrombus is a challenging high mortality disease typically seen in the setting of pulmonary embolism. Traditional treatments have included anticoagulation, thrombolysis, and surgical embolectomy. Advances in recognition and treatment of clot-in-transit have led to the development of endovascular therapies increasingly becoming the preferred method of treatment due to rapid debulking and lower morbidity. Novel endovascular devices are large bore aspiration thrombectomy systems which mitigate the use of concomitant thrombolytics. The article reviews the disease process, relevant literature, and current endovascular devices and strategies for the treatment of right heart thrombus and clot-in-transit.
Keywords: aspiration thrombectomy; pulmonary embolism; right heart thrombus.
Thieme. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest M.R. serves as the national PI for AngioDynamics Inc. APEX – AV trial assessing AlphaVac Multipurpose Mechanical Aspiration (MMA) F18 PE System in the treatment of pulmonary embolism.
Figures


References
-
- RIETE Investigators . Barrios D, Rosa-Salazar V, Jiménez D. Right heart thrombi in pulmonary embolism. Eur Respir J. 2016;48(05):1377–1385. - PubMed
-
- Goldhaber S Z, Visani L, De Rosa M.Acute pulmonary embolism: clinical outcomes in the International Cooperative Pulmonary Embolism Registry (ICOPER) Lancet 1999353(9162):1386–1389. - PubMed
-
- Muramoto H, Niwa A, Satoh Y. Clinical significance and prognosis of right heart thrombi associated with acute pulmonary thromboembolism - results of a multicenter registry of thrombolysis in Japan. Circ J. 2021;85(04):353–360. - PubMed
-
- Barkhausen J, Hunold P, Eggebrecht H. Detection and characterization of intracardiac thrombi on MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;179(06):1539–1544. - PubMed
-
- Leibowitz G, Keller N M, Daniel W G. Transesophageal versus transthoracic echocardiography in the evaluation of right atrial tumors. Am Heart J. 1995;130(06):1224–1227. - PubMed

