Ampelopsin targets in cellular processes of cancer: Recent trends and advances
- PMID: 36561961
- PMCID: PMC9764188
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2022.07.013
Ampelopsin targets in cellular processes of cancer: Recent trends and advances
Abstract
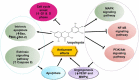
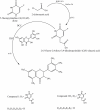
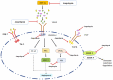
Cancer is being considered as a serious threat to human health globally due to limited availability and efficacy of therapeutics. In addition, existing chemotherapeutic drugs possess a diverse range of toxic side effects. Therefore, more research is welcomed to investigate the chemo-preventive action of plant-based metabolites. Ampelopsin (dihydromyricetin) is one among the biologically active plant-based chemicals with promising anti-cancer actions. It modulates the expression of various cellular molecules that are involved in cancer progressions. For instance, ampelopsin enhances the expression of apoptosis inducing proteins. It regulates the expression of angiogenic and metastatic proteins to inhibit tumor growth. Expression of inflammatory markers has also been found to be suppressed by ampelopsin in cancer cells. The present review article describes various anti-tumor cellular targets of ampelopsin at a single podium which will help the researchers to understand mechanistic insight of this phytochemical.
Keywords: Ampelopsin; Angiogenesis inhibition; Anti-inflammation; Anti-proliferation; Apoptotic; Cell cycle arrest.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Yang Z., Xu Y., Bi Y., Zhang N., Wang H., Xing T., Bai S., Shen Z., Naz F., Zhang Z., Yin L., Shi M., Wang L., Wang L., Wang S., Xu L., Su X., Wu S., Yu C. Immune escape mechanisms and immunotherapy of urothelial bladder cancer. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2021;7:485. doi: 10.18053/jctres.07.202104.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

