Lipomembranous fat necrosis: A distinctive and unique morphology (Review)
- PMID: 36561978
- PMCID: PMC9748762
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2022.11695
Lipomembranous fat necrosis: A distinctive and unique morphology (Review)
Abstract
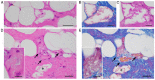
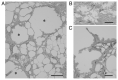
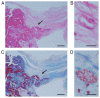
Lipomembranous fat necrosis (LFN) is an uncommon but distinct form of fat necrosis, which is characterized by eosinophilic, crenulated and/or serpiginous membranes. LFN exhibits macrocystic, microcystic and/or crushed features. LFN is routinely detectable on hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained sections, and is present both in the acute phase and in the later or fibrous stage of necrotic fatty lesions. Smaller crushed LFN embedded within fibrous tissues may be difficult to recognize on H&E-stained sections, but can be highlighted by some staining techniques, including Masson trichrome, periodic acid-Schiff, orcein, long Ziehl-Neelsen stain, silver impregnation, phosphotungstic acid-hematoxylin and luxol fast blue staining. LFN was initially considered a specific feature of Nasu-Hakola disease, but has since been identified in various subcutaneous or intraabdominal lesions related to ischemic conditions or venous insufficiency. In addition, LFN is detectable in intra-articular loose bodies and aortic valves with or without dysfunction, suggesting that LFN is also associated with ischemia-like hypoxic conditions or malnutrition. LFN is considered to be a histological hallmark of hidden ischemic or hypoxic/malnourished conditions in various diseases; however, the exact mechanisms of LFN remain poorly understood. The present review described the clinicopathological features of this interesting, but poorly characterized, condition.
Keywords: LFN; Nasu-Hakola disease; aortic valve; intraarticular loose body; ischemia; lipomembranous changes; membranocystic changes; membranous fat necrosis; soft tissue tumor.
Copyright: © Matsukuma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lipomembranous (membranocystic) fat necrosis. Clinicopathologic correlation of 38 cases.Am J Dermatopathol. 1996 Apr;18(2):151-5. doi: 10.1097/00000372-199604000-00007. Am J Dermatopathol. 1996. PMID: 8739989
-
Lipomembranous fat necrosis in three cases of testicular torsion.Histopathology. 2001 May;38(5):443-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.2001.01130.x. Histopathology. 2001. PMID: 11422481
-
Fatty lesions in intra-articular loose bodies: a histopathological study of non-primary synovial chondromatosis cases.Virchows Arch. 2012 Jan;460(1):103-8. doi: 10.1007/s00428-011-1172-0. Epub 2011 Nov 18. Virchows Arch. 2012. PMID: 22095290
-
Nasu-Hakola disease: The first case reported by Nasu and review: The 50th Anniversary of Japanese Society of Neuropathology.Neuropathology. 2010 Oct;30(5):463-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2010.01127.x. Neuropathology. 2010. PMID: 20500450 Review.
-
A case of nodular cystic fat necrosis: the end stage lesion showing calcification and lipomembranous changes.J Dermatol. 1998 Sep;25(9):616-21. J Dermatol. 1998. PMID: 9798350 Review.
Cited by
-
Implanted cartilaginous grafts following rhinoplasty: A retrospective histopathological study.Exp Ther Med. 2024 Oct 3;28(6):449. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12739. eCollection 2024 Dec. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 39421598 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brooks JSJ. Adipose tissue. In: Histology of Pathologists. Mills SE (ed). 5th edition. Wolters Kluwer, Philadelphia, PA, pp133-165, 2020.
-
- Goldblum JR, Folpe AL, Weiss SW (eds) Enzinger & Weiss's soft tissue tumors. 7th edition. Elsevier Inc., Philadelphia PA, pp225-231, 476-518, 2020.
-
- Oakes SA. Cell injury, cell death, and adaptations. In: Robbins and cotran pathologic basis of diseases. Kumar V, Abbas AK and Aster JC (eds). 10th edition. Elsevier Inc., Philadelphia PA, pp33-69, 2021.
-
- Klöppel G, von Gerkan R, Dreyer T. Pathomorphology of acute pancreatitis-analysis of 357 autopsy cases and 3 surgical specimens. In: Pancreatitis-concepts and classification. Gyr KE, Singer MV and Sarles H (eds). Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp29-35, 1984.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
