Phytochemistry, health benefits, and food applications of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.): A comprehensive review
- PMID: 36562043
- PMCID: PMC9763470
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1036295
Phytochemistry, health benefits, and food applications of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.): A comprehensive review
Abstract
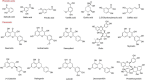
Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.), an ancient miraculous plant, is of great interest because of its tenacity, richness in nutritional active substances, and biological activity. Sea buckthorn is a deciduous shrub or tree of the genus Hippophae in the family Elaeagnaceae. It is a pioneer tree species for soil improvement, wind and sand control, and soil and water conservation. Sea buckthorn contains many nutritional active components, such as vitamins, carotenoids, polyphenols, fatty acids, and phytosterols. Moreover, sea buckthorn has many health benefits, such as antioxidant, anticancer, anti-hyperlipidemic, anti-obesity, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antiviral, dermatological, neuroprotective, and hepatoprotective activities. Sea buckthorn not only has great medicinal and therapeutic potential, but also is a promising economic plant. The potential of sea buckthorn in the human food industry has attracted the research interest of researchers and producers. The present review mainly summarizes the phytochemistry, nutrients, health benefits, and food applications of sea buckthorn. Overall, sea buckthorn is a dietary source of bioactive ingredients with the potential to be developed into functional foods or dietary supplements for the prevention and treatment of certain chronic diseases, which deserves further research.
Keywords: food applications; health benefits; nutrients; phytochemistry; sea buckthorn.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Zhao, Wei, Chai, Hou and Meng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Singh B, Peter K.. Indian sea buckthorn. New age herbals. Singapore: Springer; (2018). p. 29–54. 10.1007/978-981-10-8291-7_3 - DOI
-
- Chen X, Lian Y. The geographical distribution patterns and its formative factors on the genus Hippophae L. Acta Bot Boreali Occident Sin. (1994) 14:105–10.
-
- Stobdan T, Targais K, Lamo D, Srivastava R. Judicious use of natural resources: a case study of traditional uses of seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) in trans-himalayan ladakh. India Natl Acad Sci Lett. (2013) 36:609–13. 10.1007/s40009-013-0177-4 - DOI
-
- Piłat B, Bieniek A, Zadernowski R. Common sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) as an alternative orchard plant. Pol J Nat Sci. (2015) 30:417–30.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources