When Knowledge Is Not Enough: Applying a Behavioral Design Approach to Improve Fever Case Management in Nigeria
- PMID: 36562445
- PMCID: PMC9771460
- DOI: 10.9745/GHSP-D-22-00211
When Knowledge Is Not Enough: Applying a Behavioral Design Approach to Improve Fever Case Management in Nigeria
Abstract
Background: We sought to encourage health care providers to adhere to national malaria case management guidelines. This requires them to conduct malaria parasite tests for every patient presenting with a fever and provide malaria treatment only to those who test positive for malaria. Our goal was to make it easier for providers to follow guidelines by addressing drivers of nonadherence uncovered through facility observations and interviews with staff and clients.
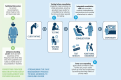
Implementation and monitoring: The case management interventions were piloted in 12 public health facilities in Akwa Ibom, Kebbi, and Nasarawa states in Nigeria between October and December 2019. Participating facilities included 1 hospital and 3 primary health centers in each state. Relevant changes included the following: (1) providers at each facility participated in facilitated discussions to correct misconceptions about the reliability of malaria test kits; (2) testing procedures were integrated into existing triage systems; (3) treatment algorithms were integrated into medical record forms; (4) providers were issued pictorial brochures outlining danger signs to share with clients, together with instructions for when to seek further care; and (5) a process was created for facilities to monitor their own adherence to guidelines.
Lessons learned: The lessons learned include: (1) disentangling the drivers of behavior allows for more targeted solutions, (2) solutions that streamline processes for overburdened providers allow them to redirect their attention and efforts where they can be most impactful, and (3) changing staff perceptions of workplace norms can support a holistic and sustained approach to behavior change.
© Haqqi et al.
Figures
References
-
- Oladosu OO, Oyibo WA. Overdiagnosis and overtreatment of malaria in children that presented with fever in Lagos, Nigeria. Int Sch Res. 2013:914675. 10.5402/2013/914675 - DOI
-
- Vogel G. Malaria-free but still sick: what’s giving millions of kids fevers? Science. March 7, 2018. Accessed November 30, 2022. https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2018/03/malaria-free-still-sick-whats-gi...
-
- Datta S, Mullainathan S. Behavioral design: a new approach to development policy. Rev Income Wealth. 2014;60(1):7–35. 10.1111/roiw.12093 - DOI
-
- Federal Republic of Nigeria. Federal Ministry of Health (FMOH). National Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Malaria. 3rd ed. FMOH; 2015. Accessed November 30, 2022. https://drive.google.com/file/d/1z2wJ0zVR6NuUCm1jkFjxl9Wnu4J-CkXU/view
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical