CLEMSite, a software for automated phenotypic screens using light microscopy and FIB-SEM
- PMID: 36562752
- PMCID: PMC9802685
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202209127
CLEMSite, a software for automated phenotypic screens using light microscopy and FIB-SEM
Abstract
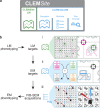
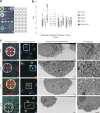
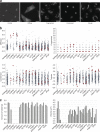
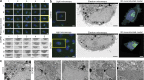
In recent years, Focused Ion Beam Scanning Electron Microscopy (FIB-SEM) has emerged as a flexible method that enables semi-automated volume ultrastructural imaging. We present a toolset for adherent cells that enables tracking and finding cells, previously identified in light microscopy (LM), in the FIB-SEM, along with the automatic acquisition of high-resolution volume datasets. We detect the underlying grid pattern in both modalities (LM and EM), to identify common reference points. A combination of computer vision techniques enables complete automation of the workflow. This includes setting the coincidence point of both ion and electron beams, automated evaluation of the image quality and constantly tracking the sample position with the microscope's field of view reducing or even eliminating operator supervision. We show the ability to target the regions of interest in EM within 5 µm accuracy while iterating between different targets and implementing unattended data acquisition. Our results demonstrate that executing volume acquisition in multiple locations autonomously is possible in EM.
© 2022 Serra Lleti et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: J.M Serra Lleti reported non-financial support from Zeiss Microscopy during the conduct of the study. “Since the developed work required control of the microscope hardware used for the experiments described in the manuscript, there was an agreement with Zeiss, that Fibics Incorporated, a third-party company from Zeiss, would provide a developer’s API able to command certain aspects of the microscope (details are described in the manuscript). The provided developer’s API was experimental and required technical support from Fibics Incorporated side. There were also meetings to discuss technical details about the operation of the microscope in the context of the project, where we benefited from the company’s expertise in FIB-SEM technology. For this reason, the API developers that provided such support are cited as co-authors (David Unrau and Mike Holtstrom).” No other disclosures were reported.
Figures






References
-
- Beckwith, M.S., Beckwith K.S., Sikorski P., Skogaker N.T., Flo T.H., and Halaas Ø.. 2015. Seeing a mycobacterium-infected cell in nanoscale 3D: Correlative imaging by light microscopy and FIB/SEM tomography. PLoS One. 10:e0134644. 10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.013464410.1371/journal.pone.0134644 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carpenter, A.E., Jones T.R., Lamprecht M.R., Clarke C., Kang I.H., Friman O., Guertin D.A., Chang J.H., Lindquist R.A., Moffat J., et al. . 2006. CellProfiler: Image analysis software for identifying and quantifying cell phenotypes. Genome Biol. 7:R100. 10.1186/gb-2006-7-10-r100 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

