Sinus node dysfunction: current understanding and future directions
- PMID: 36563014
- PMCID: PMC9886352
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00618.2022
Sinus node dysfunction: current understanding and future directions
Abstract
The sinoatrial node (SAN) is the primary pacemaker of the heart. Normal SAN function is crucial in maintaining proper cardiac rhythm and contraction. Sinus node dysfunction (SND) is due to abnormalities within the SAN, which can affect the heartbeat frequency, regularity, and the propagation of electrical pulses through the cardiac conduction system. As a result, SND often increases the risk of cardiac arrhythmias. SND is most commonly seen as a disease of the elderly given the role of degenerative fibrosis as well as other age-dependent changes in its pathogenesis. Despite the prevalence of SND, current treatment is limited to pacemaker implantation, which is associated with substantial medical costs and complications. Emerging evidence has identified various genetic abnormalities that can cause SND, shedding light on the molecular underpinnings of SND. Identification of these molecular mechanisms and pathways implicated in the pathogenesis of SND is hoped to identify novel therapeutic targets for the development of more effective therapies for this disease. In this review article, we examine the anatomy of the SAN and the pathophysiology and epidemiology of SND. We then discuss in detail the most common genetic mutations correlated with SND and provide our perspectives on future research and therapeutic opportunities in this field.
Keywords: automaticity; pacemaker; sinus node dysfunction.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures
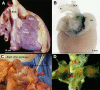
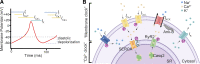
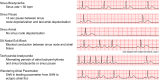
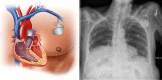
References
-
- Kusumoto FM, Schoenfeld MH, Barrett C, Edgerton JR, Ellenbogen KA, Gold MR, Goldschlager NF, Hamilton RM, Joglar JA, Kim RJ, Lee R, Marine JE, McLeod CJ, Oken KR, Patton KK, Pellegrini CN, Selzman KA, Thompson A, Varosy PD. 2018 ACC/AHA/HRS guideline on the evaluation and management of patients with bradycardia and cardiac conduction delay: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation 140: e382, 2019. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein AD, Parsonnet V. Survey of cardiac pacing and defibrillation in the United States in 1993. Am J Cardiol 78: 187–196, 1996. - PubMed
-
- Hayes DL, Asirvatham SJ, Friedman PA. Cardiac Pacing, Defibrillation and Resynchronization a Clinical Approach. Chichester, UK: Wiley-Blackwell, 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

