Circulating hemopexin modulates anthracycline cardiac toxicity in patients and in mice
- PMID: 36563141
- PMCID: PMC9788780
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adc9245
Circulating hemopexin modulates anthracycline cardiac toxicity in patients and in mice
Abstract
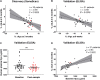
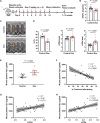
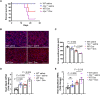
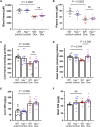
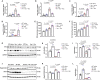
Anthracyclines such as doxorubicin (Dox) are effective chemotherapies, but their use is limited by cardiac toxicity. We hypothesized that plasma proteomics in women with breast cancer could identify new mechanisms of anthracycline cardiac toxicity. We measured changes in 1317 proteins in anthracycline-treated patients (n = 30) and replicated key findings in a second cohort (n = 31). An increase in the heme-binding protein hemopexin (Hpx) 3 months after anthracycline initiation was associated with cardiac toxicity by echocardiography. To assess the functional role of Hpx, we administered Hpx to wild-type (WT) mice treated with Dox and observed improved cardiac function. Conversely, Hpx-/- mice demonstrated increased Dox cardiac toxicity compared to WT mice. Initial mechanistic studies indicate that Hpx is likely transported to the heart by circulating monocytes/macrophages and that Hpx may mitigate Dox-induced ferroptosis to confer cardioprotection. Together, these observations suggest that Hpx induction represents a compensatory response during Dox treatment.
Figures


References
-
- P. Vejpongsa, E. T. Yeh,Prevention of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity: Challenges and opportunities. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 64,938–945 (2014). - PubMed
-
- D. Cardinale, A. Colombo, G. Bacchiani, I. Tedeschi, C. A. Meroni, F. Veglia, M. Civelli, G. Lamantia, N. Colombo, G. Curigliano, C. Fiorentini, C. M. Cipolla,Early detection of anthracycline cardiotoxicity and improvement with heart failure therapy. Circulation 131,1981–1988 (2015). - PubMed
-
- G. H. Oliveira, M. Dupont, D. Naftel, S. L. Myers, Y. Yuan, W. H. Tang, G. Gonzalez-Stawinski, J. B. Young, D. O. Taylor, R. C. Starling,Increased need for right ventricular support in patients with chemotherapy-induced cardiomyopathy undergoing mechanical circulatory support: Outcomes from the INTERMACS Registry (Interagency Registry for Mechanically Assisted Circulatory Support). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 63,240–248 (2014). - PubMed
-
- D. Cardinale, M. T. Sandri, A. Colombo, N. Colombo, M. Boeri, G. Lamantia, M. Civelli, F. Peccatori, G. Martinelli, C. Fiorentini, C. M. Cipolla,Prognostic value of troponin I in cardiac risk stratification of cancer patients undergoing high-dose chemotherapy. Circulation 109,2749–2754 (2004). - PubMed
-
- B. G. Demissei, R. A. Hubbard, L. Zhang, A. M. Smith, K. Sheline, C. McDonald, V. Narayan, S. M. Domchek, A. DeMichele, P. Shah, A. S. Clark, K. Fox, J. Matro, A. R. Bradbury, H. Knollman, K. D. Getz, S. H. Armenian, J. L. Januzzi, W. H. W. Tang, P. Liu, B. Ky,Changes in cardiovascular biomarkers with breast cancer therapy and associations with cardiac dysfunction. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 9,e014708 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

