Nivolumab and brentuximab vedotin with or without bendamustine for R/R Hodgkin lymphoma in children, adolescents, and young adults
- PMID: 36564047
- PMCID: PMC10646780
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2022017118
Nivolumab and brentuximab vedotin with or without bendamustine for R/R Hodgkin lymphoma in children, adolescents, and young adults
Abstract
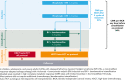
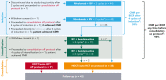
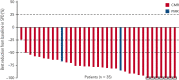
Children, adolescents, and young adults (CAYA) with relapsed/refractory (R/R) classic Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) without complete metabolic response (CMR) before autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation (auto-HCT) have poor survival outcomes. CheckMate 744, a phase 2 study for CAYA (aged 5-30 years) with R/R cHL, evaluated a risk-stratified, response-adapted approach with nivolumab plus brentuximab vedotin (BV) followed by BV plus bendamustine for patients with suboptimal response. Risk stratification was primarily based on time to relapse, prior treatment, and presence of B symptoms. We present the primary analysis of the standard-risk cohort. Data from the low-risk cohort are reported separately. Patients received 4 induction cycles with nivolumab plus BV; those without CMR (Deauville score >3, Lugano 2014) received BV plus bendamustine intensification. Patients with CMR after induction or intensification proceeded to consolidation (high-dose chemotherapy/auto-HCT per protocol). Primary end point was CMR any time before consolidation. Forty-four patients were treated. Median age was 16 years. At a minimum follow-up of 15.6 months, 43 patients received 4 induction cycles (1 discontinued), 11 of whom received intensification; 32 proceeded to consolidation. CMR rate was 59% after induction with nivolumab plus BV and 94% any time before consolidation (nivolumab plus BV ± BV plus bendamustine). One-year progression-free survival rate was 91%. During induction, 18% of patients experienced grade 3/4 treatment-related adverse events. This risk-stratified, response-adapted salvage strategy had high CMR rates with limited toxicities in CAYA with R/R cHL. Most patients did not require additional chemotherapy (bendamustine intensification). Additional follow-up is needed to confirm durability of disease control. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT02927769.
© 2023 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: C.M.-K. received research grants, payment/honoraria for lectures, presentations, and payment for participation on a data safety monitoring board from Merck Sharp and Dohme; and is the Scientific Secretary (unpaid) of the EuroNet–Paediatric Hodgkin Lymphoma Consortium. T.L. received payment for travel and accommodation from Bristol Myers Squibb. G.M. received payment for participation in the study protocol from Bristol Myers Squibb. S.C. received payment/honoraria from Jazz Pharmaceuticals and Pfizer for lectures, presentations, speaker’s bureaus, manuscript writing, or educational events, and payment from Covington LLC for expert testimony. K.J.L. received research grants from Abbott Laboratories, consulting fees from Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and payment from BTG and Jazz Pharmaceuticals for participation on an advisory board. B.S.H. received funding from Merck via the Children’s Oncology Group for participation on a data safety monitoring board/advisory board. J.L. has equity interest and is an employee of Seagen, Inc. S.F. has stock options and was an employee of Bristol Myers Squibb. M.S. was an employee of Bristol Myers Squibb. K.M.K. received payment from Merck via the Children’s Oncology Group for participation on a study steering committee and is a member on the scientific advisory board (unpaid) for Lymphoma Research Foundation. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Queen's gambit: response-adapted win in CAYA with cHL.Blood. 2023 Apr 27;141(17):2037-2038. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022019339. Blood. 2023. PMID: 37103949 No abstract available.

