Unique roles of co-receptor-bound LCK in helper and cytotoxic T cells
- PMID: 36564464
- PMCID: PMC9810533
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-022-01366-0
Unique roles of co-receptor-bound LCK in helper and cytotoxic T cells
Abstract
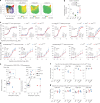
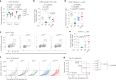
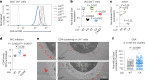
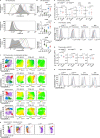
The kinase LCK and CD4/CD8 co-receptors are crucial components of the T cell antigen receptor (TCR) signaling machinery, leading to key T cell fate decisions. Despite decades of research, the roles of CD4-LCK and CD8-LCK interactions in TCR triggering in vivo remain unknown. In this study, we created animal models expressing endogenous levels of modified LCK to resolve whether and how co-receptor-bound LCK drives TCR signaling. We demonstrated that the role of LCK depends on the co-receptor to which it is bound. The CD8-bound LCK is largely dispensable for antiviral and antitumor activity of cytotoxic T cells in mice; however, it facilitates CD8+ T cell responses to suboptimal antigens in a kinase-dependent manner. By contrast, the CD4-bound LCK is required for efficient development and function of helper T cells via a kinase-independent stabilization of surface CD4. Overall, our findings reveal the role of co-receptor-bound LCK in T cell biology, show that CD4- and CD8-bound LCK drive T cell development and effector immune responses using qualitatively different mechanisms and identify the co-receptor-LCK interactions as promising targets for immunomodulation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures












Comment in
-
Bound to be perfect: Lck and T cell co-receptors.Nat Immunol. 2023 Jan;24(1):5-7. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01392-y. Nat Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36596893 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

