International monitoring of capacity of treatment systems for alcohol and drug use disorders: Methodology of the Service Capacity Index for Substance Use Disorders
- PMID: 36564954
- PMCID: PMC10485318
- DOI: 10.1002/mpr.1950
International monitoring of capacity of treatment systems for alcohol and drug use disorders: Methodology of the Service Capacity Index for Substance Use Disorders
Abstract
Objectives: We aimed to develop a Service Capacity Index for Substance Use Disorders (SCI-SUD) that would reflect the capacity of national health systems to provide treatment for alcohol and drug use disorders, in terms of the proportion of available service elements in a given country from a theoretical maximum.
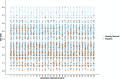
Methods: Data were collected through the WHO Global Survey on Progress with Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) Health Target 3.5, conducted between December 2019 and July 2020 to produce the SCI-SUD, based on 378 variables overall.
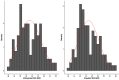
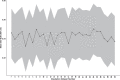
Results: The SCI-SUD was directly derived for 145 countries. We used multiple imputation to produce comparable SCI-SUD estimates for countries that did not submit data (40 countries) or had very high level of missingness (9 countries). The final SCI-SUD demonstrates considerable consistency and internal stability and is strongly associated with the macro-level economic, healthcare-related and epidemiologic (such as prevalence rates) variables.
Conclusion: The presented methodology represents a step forward in monitoring the global situation in regard to the development of treatment systems for SU disorders, however, further work is warranted to improve the external validity of the measure (e.g., in-depth data generation in countries) and ensure its feasibility for regular reporting (e.g., reducing the number of variables).
Keywords: global estimates; global monitoring; health systems; service capacity; substance use disorders.
© 2022 World Health Organization; licensed by John Wiley & Sons Ltd. International Journal of Methods in Psychiatric Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors alone are responsible for the views expressed in this article and they do not necessarily represent the views, decisions or policies of the institutions with which they are affiliated. The authors declare there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Babor, T. F. , & Poznyak, V. (2010). The World health organization substance abuse instrument for mapping services: Rationale, structure and functions. Nordic Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 27(6), 703–712. 10.1177/145507251002700614 - DOI
-
- Degenhardt, L. , Glantz, M. , Evans‐Lacko, S. , Sadikova, E. , Sampson, N. , Thornicroft, G. , Aguilar‐Gaxiola, S. , Al‐Hamzawi, A. , Alonso, J. , Helena Andrade, L. , Bruffaerts, R. , Bunting, B. , Bromet, E. J. , de Miguel Caldas Almeida, J. , de Girolamo, G. , Florescu, S. , Gureje, O. , Maria Haro, J. , Huang, Y. , … World Health Organization's World Mental Health Surveys collaborators . (2017). Estimating treatment coverage for people with substance use disorders: An analysis of data from the World mental health surveys. World Psychiatry, 16(3), 299–307. 10.1002/wps.20457 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

