On-Treatment Platelet Reactivity and Ischemic Outcomes in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus: Two-Year Results From ADAPT-DES
- PMID: 36565189
- PMCID: PMC9973569
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.122.026482
On-Treatment Platelet Reactivity and Ischemic Outcomes in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus: Two-Year Results From ADAPT-DES
Abstract
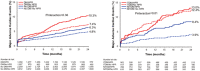
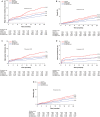
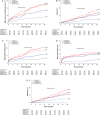
Background Diabetes mellitus and high platelet reactivity (HPR) on clopidogrel are both associated with increased risk of ischemic events after percutaneous coronary intervention, but whether the HPR-associated risk of adverse ischemic events differs by diabetes mellitus status is unknown. Methods and Results ADAPT-DES (Assessment of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy With Drug-Eluting Stents) was a prospective, multicenter registry of patients treated with coronary drug-eluting stents. HPR was defined as P2Y12 reaction units >208 by the VerifyNow point-of-care assay. Cox multivariable analysis was used to assess whether HPR-associated risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACE; cardiac death, myocardial infarction, or stent thrombosis) varied for patients with insulin-treated diabetes mellitus (ITDM), non-ITDM, and no diabetes mellitus. Diabetes mellitus and HPR were included in an interaction analysis. Of 8582 patients enrolled, 2429 (28.3%) had diabetes mellitus, of whom 998 (41.1%) had ITDM. Mean P2Y12 reaction units were higher in patients with diabetes mellitus versus without diabetes mellitus, and HPR was more frequent in patients with diabetes mellitus. HPR was associated with consistently increased 2-year rates of MACE in patients with and without diabetes mellitus (Pinteraction=0.36). A significant interaction was present between HPR and non-insulin-treated diabetes mellitus versus ITDM for 2-year MACE (adjusted hazard ratio [HR] for non-ITDM, 2.28 [95% CI, 1.39-3.73] versus adjusted HR for ITDM, 1.02 [95% CI, 0.70-1.50]; Pinteraction=0.01). Conclusions HPR was more common in patients with diabetes mellitus and was associated with an increased risk of MACE in both patients with and without diabetes mellitus. In patients with diabetes mellitus, a more pronounced effect of HPR on MACE was present in lower-risk non-ITDM patients than in higher-risk patients with ITDM. Registration URL: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00638794; Unique identifier: NCT00638794. ADAPT-DES (Assessment of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy With Drug-Eluting Stents).
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; drug‐eluting stent; percutaneous coronary intervention; platelet reactivity.
Figures
References
-
- Brar SS, ten Berg J, Marcucci R, Price MJ, Valgimigli M, Kim HS, Patti G, Breet NJ, DiSciascio G, Cuisset T, et al. Impact of platelet reactivity on clinical outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention. A collaborative meta‐analysis of individual participant data. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58:1945–1954. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.06.059 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stone GW, Witzenbichler B, Weisz G, Rinaldi MJ, Neumann FJ, Metzger DC, Henry TD, Cox DA, Duffy PL, Mazzaferri E, et al. Platelet reactivity and clinical outcomes after coronary artery implantation of drug‐eluting stents (ADAPT‐DES): a prospective multicentre registry study. Lancet. 2013;382:614–623. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61170-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Angiolillo DJ, Bernardo E, Ramirez C, Costa MA, Sabate M, Jimenez‐Quevedo P, Hernandez R, Moreno R, Escaned J, Alfonso F, et al. Insulin therapy is associated with platelet dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on dual oral antiplatelet treatment. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48:298–304. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.03.038 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Angiolillo DJ, Fernandez‐Ortiz A, Bernardo E, Ramirez C, Sabate M, Jimenez‐Quevedo P, Hernandez R, Moreno R, Escaned J, Alfonso F, et al. Platelet function profiles in patients with type 2 diabetes and coronary artery disease on combined aspirin and clopidogrel treatment. Diabetes. 2005;54:2430–2435. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.54.8.2430 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

