Microfluidic liquid sheets as large-area targets for high repetition XFELs
- PMID: 36567947
- PMCID: PMC9780453
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1048932
Microfluidic liquid sheets as large-area targets for high repetition XFELs
Abstract
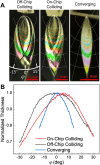
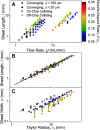
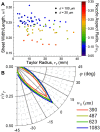
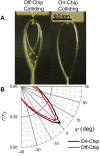
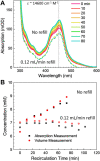
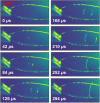
The high intensity of X-ray free electron lasers (XFELs) can damage solution-phase samples on every scale, ranging from the molecular or electronic structure of a sample to the macroscopic structure of a liquid microjet. By using a large surface area liquid sheet microjet as a sample target instead of a standard cylindrical microjet, the incident X-ray spot size can be increased such that the incident intensity falls below the damage threshold. This capability is becoming particularly important for high repetition rate XFELs, where destroying a target with each pulse would require prohibitively large volumes of sample. We present here a study of microfluidic liquid sheet dimensions as a function of liquid flow rate. Sheet lengths, widths and thickness gradients are shown for three styles of nozzles fabricated from isotropically etched glass. In-vacuum operation and sample recirculation using these nozzles is demonstrated. The effects of intense XFEL pulses on the structure of a liquid sheet are also briefly examined.
Keywords: devices; instruments; liquid microjets; microfluidics; samples; spectroscopy; structural biology; x-ray.
Copyright © 2022 Hoffman, Van Driel, Kroll, Crissman, Ryland, Nelson, Cordones, Koralek and DePonte.
Conflict of interest statement
The converging type nozzle described in this work has been licensed to Micronit Ltd. for which Stanford, SLAC, and DD may receive a portion of royalty payments related to product sales. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bush J. W. M., Hasha A. E. (2004). On the collision of laminar jets: Fluid chains and fishbones. J. Fluid Mech. 511, 285–310. 10.1017/s002211200400967x - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

