Stigma mastery in people living with HIV: gender similarities and theory
- PMID: 36567981
- PMCID: PMC9788541
- DOI: 10.1007/s10389-021-01480-7
Stigma mastery in people living with HIV: gender similarities and theory
Abstract
Aims: This study aimed to determine the prevalence of, factors associated with, and to build a theoretical framework for understanding Internalsed HIV-related Stigma Mastery (IHSM).
Methods: A cross-sectional study nested within a 2014 Stigma Reduction Cohort in Uganda was used. The PLHIV Stigma Index version 2008, was used to collect data from a random sample of 666 people living with HIV (PLHIV) stratified by gender and age. SPSS24 with Amos27 softwares were used to build a sequential-mediation model.
Results: The majority of participants were women (65%), aged ≥ 40 years (57%). Overall, IHSM was 45.5% among PLHIV, that increased with age. Specifically, higher IHSM correlated with men and older women "masculine identities" self-disclosure of HIV-diagnosis to family, sharing experiences with peers. However, lower IHSM correlated with feminine gender, the experience of social exclusion stress, fear of future rejection, and fear of social intimacy. Thus, IHSM social exclusion with its negative effects and age-related cognition are integrated into a multidimensional IHSM theoretical framework with a good model-to-data fit.
Conclusion: Internalised HIV-related Stigma Mastery is common among men and older women. Specificially, "masculine identities" self-disclose their own HIV-positive diagnosis to their family, share experiences with peers to create good relationships for actualising or empowerment in stigma mastery. However, social exclusion exacerbates series of negative effects that finally undermine stigma mastery by young feminine identities. Thus, stigma mastery is best explained by an integrated empowerment framework, that has implications for future practice, policy, and stigma-related research that we discuss.
Keywords: HIV-related; gender; mastery; similarities; stigma; theory-building.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures
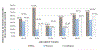

References
-
- Arbuckle J (2013) IBM SPSS AMOS 22 users’ guide. IBM Corp. Amos Development Corporation, Crawfordville
-
- Arnold M, Benton A, Loveluck J, Skipper S, Sprague L (2016) The U.S. people living with HIV stigma index: Michigan: wave 1 findings, 2014–2016. UNIFIED-HIV Health and Beyond, Detroit
-
- Bandura A (1999) Social cognitive theory of personality. In: John OP, Pervin LA (eds) Handbook of personality, vol 2, 3rd edn. The Guilford Press, New York, pp 154–196
-
- Baumeister R, Tice D (1990) Point-counterpoints: anxiety and social exclusion. J Soc Clin Psychol 9:165–195. 10.1521/jscp.1990.9.2.165 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
