Two novel mutations in VPS33B gene cause a milder ARC syndrome with prolonged survival in a 12-year-old patient: Case report
- PMID: 36568436
- PMCID: PMC9768213
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.1041080
Two novel mutations in VPS33B gene cause a milder ARC syndrome with prolonged survival in a 12-year-old patient: Case report
Abstract
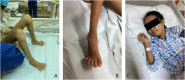
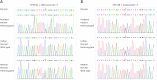
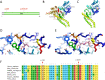
Arthrogryposis-renal dysfunction-cholestasis (ARC) syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive disease caused by VPS33B and VIPAR gene mutations. The main clinical manifestations are congenital joint contracture, renal dysfunction mainly characterized by distal renal tubular dysfunction, and low glutamyltransferase cholestasis. Most patients with ARC die within 2 years of birth. Here, we report the case of a 12-year-old girl with an ARC phenotype who experienced long-term survival with only mild clinical symptoms. We detected two new heterozygous mutation sites of the VPS33B gene in this child, c.1081C > T (p.GLN361X, 257) and c.244T > C (p.Cys82Arg), through the gene detection technique; the tertiary structure of the protein was predicted by using the SWISS-model. We further reviewed the literature and summarized the clinical manifestations and gene loci of 19 ARC syndrome patients with long-term survival reported so far.
Keywords: ARC syndrome; VPS33B; genetics; novel mutation; prolonged survival.
© 2022 Zhu and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

