Massive Congestive Facial and Submandibular Oedema Due to Extreme Neck Flexion Following Suboccipital Craniectomy: A Case Report
- PMID: 36569736
- PMCID: PMC9775002
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.31759
Massive Congestive Facial and Submandibular Oedema Due to Extreme Neck Flexion Following Suboccipital Craniectomy: A Case Report
Abstract
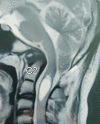
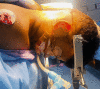
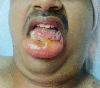
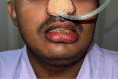
A variety of factors could contribute to facial oedema during a prone neurosurgical procedure. For optimal surgical exposure, suboccipital cranial surgeries frequently necessitate extreme neck flexion. Extreme neck flexion in the prone position can impair venous drainage of the facial and oropharyngeal structures, leading to life-threatening oedema, so a two-fingerbreadth space between the chin and the sternum is critical. We present a case of massive facial oedema with submandibular swelling in a patient who underwent foramen magnum decompression in the prone position for Arnold Chiari malformation.
Keywords: arnold chiari malformation; congestive oedema; neck flexion; submandibular swelling; suboccipital craniectomy.
Copyright © 2022, Vaithialingam et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Vectored cranial-cervical traction limits facial contact pressure from prone positioning during posterior spinal deformity surgery. Koreckij J, Price N, Schwend RM. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2011;36:0–7. - PubMed
-
- Delayed airway obstruction in posterior fossa craniotomy with park-bench position—a case report and review of the literatures. Hsu S, Hsieh C, Huang C, Huang J. Surg Sci. 2012;3:526–529.
-
- Oropharyngeal swelling and macroglossia after cervical spine surgery in the prone position. Sinha A, Agarwal A, Gaur A, Pandey CK. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2001;13:237–239. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
