Desire to stay shorter time at the shopping mall: insight from protection motivation (PMT), behavioral inhibition system (BIS), reactance, and expectancy theories
- PMID: 36570056
- PMCID: PMC9759057
- DOI: 10.1007/s12144-022-04117-4
Desire to stay shorter time at the shopping mall: insight from protection motivation (PMT), behavioral inhibition system (BIS), reactance, and expectancy theories
Abstract
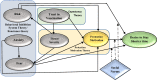
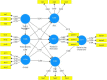
After withdrawing the movement control order (MCO), new variant (Omicron) of COVID-19 returns as an outbreak again. Therefore, consumers are very much informed by various media to be more cautious in visiting shopping malls and spend less time in there. The purpose of this study was to identify the predictors influencing the desire to stay shorter at the shopping mall. This study was conducted in Malaysia, with the application of three psychological theories and one behavioural theory. This is quantitative research based on an online cross-sectional survey design. Data were collected from 296 respondents, by applying the online snowball sampling method through numerous media platforms i.e., Viber, WhatsApp, Messenger, and other apps in three severely affected cities in Malaysia i.e., Selangor state, Putrajaya, and Kuala Lumpur. SmartPLS was used to analyse the data. Using structural equation modelling, this study result shows risk, protection motivation, and fear have a significant effect on the desire to stay a shorter time at the shopping mall. Social norm moderates the association between fear and the desire to spend a shorter time at the shopping mall. These findings, highlight the need for a more empirical study to design more robust strategies, and a safer and risk-free shopping mall environment.
Keywords: Desire to stay shorter; Protection motivation; Social norms; Trust in vaccination.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluating the influence of service quality, hedonic, and utilitarian value on shopper's behavioral intentions in urban shopping malls during the COVID-19 pandemic.Heliyon. 2022 Dec;8(12):e12542. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12542. Epub 2022 Dec 20. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36568661 Free PMC article.
-
Sanitary conditions, waste management, safety measures and sources of air pollution associated with shopping malls in Nigeria's largest city.Public Health Pract (Oxf). 2023 Feb 24;5:100376. doi: 10.1016/j.puhip.2023.100376. eCollection 2023 Jun. Public Health Pract (Oxf). 2023. PMID: 36937096 Free PMC article.
-
Rehabilitation in the real-life environment of a shopping mall.Disabil Rehabil. 2018 Apr;40(7):848-855. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2016.1277394. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Disabil Rehabil. 2018. PMID: 28129514
-
A Smartphone-Based Shopping Mall Walking Program and Daily Walking Steps.JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Jan 2;7(1):e2353957. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.53957. JAMA Netw Open. 2024. PMID: 38289599 Free PMC article.
-
Protection Motivation Theory and consumers' food safety behaviour in response to COVID-19.Food Control. 2022 Aug;138:109029. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2022.109029. Epub 2022 Apr 14. Food Control. 2022. PMID: 35449723 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ajzen I. The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes. 1991;50:179–211. doi: 10.1016/0749-5978(91)90020-T. - DOI
-
- Al Amin Md, Arefin MS, Sultana N, Islam MR, Jahan I, Akhtar A. Evaluating the customers’ dining attitudes, e-satisfaction and continuance intention toward mobile food ordering apps (MFOAs): Evidence from Bangladesh. European Journal of Management and Business Economics. 2020;30(2):85–103.
-
- Alam SS, Sayuti NM. Applying the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) in halal food purchasing. International Journal of Commerce and Management. 2011;21(1):8–21. doi: 10.1108/10569211111111676. - DOI
-
- Amin M, Ryu K, Cobanoglu C, Rezaei S, Wulan MM. Examining the effect of shopping mall attributes in predicting tourist shopping satisfaction and behavioral intentions: Variation across generation X and Y. Journal of Quality Assurance in Hospitality & Tourism. 2021;22(3):367–394. doi: 10.1080/1528008X.2020.1818667. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous