Assessment of Hearing Loss in Minor Head Injury: A Prospective Study
- PMID: 36570745
- PMCID: PMC9771613
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0042-1757431
Assessment of Hearing Loss in Minor Head Injury: A Prospective Study
Abstract
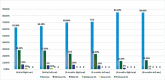
Introduction Hearing loss following a head injury is common and well known. The numbers of road traffic accidents have increased recently, with minor head injuries being very common, and usually go unreported. Hearing loss after a minor head injury is often unnoticed. Available literature is limited in this regard. Objective This study was done to assess hearing loss in patients with minor head injuries and to define its natural history and progression/regression by a serial assessment of hearing. Methods This prospective study was done in the Department of Neurosurgery, AIIMS, Bhubaneshwar, Odisha, India, for a period of 24 months to look at the profile of hearing levels of patients presenting with history suggestive of minor head injury. Results This study has shown that some form of hearing loss is common after a minor head injury and should be evaluated in all patients to detect subclinical hearing loss. A significant number of patients having minimal or a mild degree of hearing loss, if managed properly, improve to preinjury status. Distortion product oto-acoustic emission testing should be used as the screening and follow-up tool. Conclusion This study highlights the importance of hearing assessment in minor-head-injury patients and the prognosis of recovery as per the severity of hearing loss and head injury.
Keywords: hearing assessment; hearing loss; minor head injury; outcome; road traffic accidents.
Asian Congress of Neurological Surgeons. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Schuknecht H F. Mechanism of inner ear injury from blows to the head. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1969;78(02):253–262. - PubMed
-
- Yetiser S, Hidir Y, Gonul E. Facial nerve problems and hearing loss in patients with temporal bone fractures: demographic data. J Trauma. 2008;65(06):1314–1320. - PubMed
-
- Browning G G, Swan I R, Gatehouse S. Hearing loss in minor head injury. Arch Otolaryngol. 1982;108(08):474–477. - PubMed
-
- Munjal S K, Panda N K, Pathak A.Audiological deficits after closed head injury J Trauma 2010680113–18., discussion 18 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources