Fulminant Retropharyngeal Edema Associated with SARS-COV-2 (+) Diagnosis in an Adult
- PMID: 36571099
- PMCID: PMC9758676
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-022-03374-w
Fulminant Retropharyngeal Edema Associated with SARS-COV-2 (+) Diagnosis in an Adult
Abstract
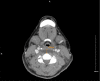
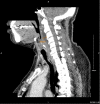
SARS-COV-2 can cause retropharyngeal edema for which literature on optimal management is sparse. Prompt identification and treatment of the condition is vital to successful recovery. This report presents such a case and offers support for conservative management in treatment of retropharyngeal edema.
Keywords: Conservative management; Retropharyngeal edema; Retropharyngeal space; SARS-COV-2.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2022. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to report, including financial or non-financial interests that may otherwise be directly or indirectly related to this work.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous