Coronavirus disease 2019 rebounds following nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment
- PMID: 36571273
- PMCID: PMC9880661
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.28430
Coronavirus disease 2019 rebounds following nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment
Abstract
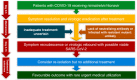
Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (NMV-r) is an effective anti-SARS-CoV-2 agent and has been recommended in the treatment of nonhospitalized patients with COVID-19. In rare occasions, some patients experience virologic and symptomatic rebound after initial resolution, which we call COVID-19 rebound after NMV-r. Although COVID rebound can also occur after molnupiravir treatment or even no antiviral treatment, we have more serious concern about the rebound after NMV-r, which remains the most effective antiviral. Due to a lack of information about its frequency, mechanism, outcomes, and management, we conducted this review to provide comprehensive and updated information to address these questions. Based on the limited evidence, the incidence of COVID-19 rebound after NMV-r was less than 2%, and most cases developed 5-15 days after initiating NMV-r treatment. Almost all reported cases had mild symptoms, and the clinical condition gradually subsided without additional treatment. Overall, the clinical outcome was favorable, and only a small number of patients required emergency department visits or hospitalization. Regarding virologic rebound, culturable SARS-CoV-2 with possible transmission was observed, so re-isolation may be needed.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; mechanisms; nirmatrelvir/ritonavir; rebound; virological rebound.
© 2022 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest declared
Figures
References
-
- Lai CC, Chen IT, Chao CM, Lee PI, Ko WC, Hsueh PR. COVID‐19 vaccines: concerns beyond protective efficacy and safety. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2021;20:1013‐1025. - PubMed
-
- Bestetti RB, Furlan‐Daniel R, Couto LB. Nonpharmaceutical public health interventions to curb the COVID‐19 pandemic: a narrative review. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2022;16:583‐591. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous