Barriers and opportunities for gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer therapy
- PMID: 36571444
- PMCID: PMC9925166
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00331.2022
Barriers and opportunities for gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer therapy
Abstract
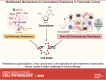
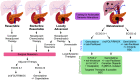
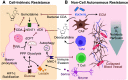
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) has become one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths across the world. A lack of durable responses to standard-of-care chemotherapies renders its treatment particularly challenging and largely contributes to the devastating outcome. Gemcitabine, a pyrimidine antimetabolite, is a cornerstone in PDA treatment. Given the importance of gemcitabine in PDA therapy, extensive efforts are focusing on exploring mechanisms by which cancer cells evade gemcitabine cytotoxicity, but strategies to overcome them have not been translated into patient care. Here, we will introduce the standard treatment paradigm for patients with PDA, highlight mechanisms of gemcitabine action, elucidate gemcitabine resistance mechanisms, and discuss promising strategies to circumvent them.
Keywords: chemoresistance; gemcitabine; metabolism; pancreatic cancer; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures

References
-
- Burris HA 3rd, Moore MJ, Andersen J, Green MR, Rothenberg ML, Modiano MR, Cripps MC, Portenoy RK, Storniolo AM, Tarassoff P, Nelson R, Dorr FA, Stephens CD, Hoff DD. Improvements in survival and clinical benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with advanced pancreas cancer: a randomized trial. J Clin Oncol 15: 2403–2413, 1997. doi:10.1200/JCO.1997.15.6.2403. - DOI - PubMed
-
- NCCN Guidelines (Online). National Comprehensive Cancer Network. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/pancreatic.pdf [2022 Nov 20].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

