The wound healing effect of collagen/adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) hydrogel: In vivo study
- PMID: 36571812
- PMCID: PMC9856998
- DOI: 10.1002/vms3.1059
The wound healing effect of collagen/adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) hydrogel: In vivo study
Abstract
Background: The complex wound healing process involves activating and synchronizing intracellular, intercellular, and extracellular components. Adipose tissue is attracting attention to promote wound healing. Within subcutaneous adipose tissue, stromal vascular cells and their subsets release growth factors and cytokines critical for neovascularization and wound repair.
Objectives: This study evaluated human placental collagen/adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) hydrogel for wound healing in rats.
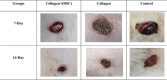
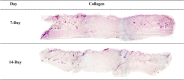
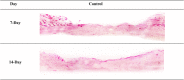
Methods: In this study, ADSCs were harvested, cultured, and mixed with placental collagen. Twelve rats were used, and their backs were excised three times each. Group one received collagen/ADSCs, group two collagen, and group three non-filled (control) excisions. The healing processes were assessed by histological analysis, taking photographs, and calculating the percentage of wound contraction in mentioned times.
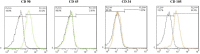
Results: Histopathological analysis revealed that the content of fibroblasts, follicles of the hair, and angiogenesis in group one was significantly more than in other groups. Group one had a significant result compared with the collagen and control groups. In group one, significant wound healing and wound contraction were observed with 52% and 80% wound contraction at 7 and 14 days, respectively.
Conclusion: Collagen/ADSCs can be considered a suitable candidate hydrogel in wound healing with a high potential for enhancing wound repairing.
Keywords: ADSCs; Wound healing; collagen; hydrogel; placenta.
© 2022 The Authors. Veterinary Medicine and Science published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Effects of hypoxia-pretreated rat adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells conditioned medium on wound healing of rats with full-thickness defects].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020 Sep 20;36(9):803-812. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20200508-00258. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32972065 Chinese.
-
[Experimental study on adipose derived stem cells combined with chitosan chloride hydrogel for treating deep partial thickness scald in rats].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Jan 15;33(1):101-109. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201804109. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30644269 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Effects of rabbit adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on the healing of skin deep partial-thickness scald wound of rabbit].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2016 Jul 20;32(7):402-7. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2016.07.004. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27464630 Chinese.
-
Prospective application of exosomes derived from adipose-derived stem cells in skin wound healing: A review.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020 Mar;19(3):574-581. doi: 10.1111/jocd.13215. Epub 2019 Nov 21. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 31755172 Review.
-
Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells and application to skin wound healing.Cell Prolif. 2021 Mar;54(3):e12993. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12993. Epub 2021 Jan 17. Cell Prolif. 2021. PMID: 33458899 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oral Complications Associated with the Piercing of Oral and Perioral Tissues and the Corresponding Degree of Awareness among Public and Professionals: A Systematic Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Nov 2;13(21):3371. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13213371. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells in craniofacial reconstruction: a comprehensive review.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Apr 16;11:1362338. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1362338. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38690295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a Composite Hydrogel Containing Statistically Optimized PDGF-Loaded Polymeric Nanospheres for Skin Regeneration: In Vitro Evaluation and Stem Cell Differentiation Studies.ACS Omega. 2024 Mar 19;9(13):15114-15133. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c09391. eCollection 2024 Apr 2. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38585049 Free PMC article.
-
Bevacizumab, a vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor, promotes orthodontic tooth movement in an experimental rat model.Heliyon. 2023 May 12;9(5):e16217. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16217. eCollection 2023 May. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37215827 Free PMC article.
-
3D-printed PCL scaffolds with anatomy-inspired bionic stratified structures for the treatment of growth plate injuries.Mater Today Bio. 2023 Oct 19;23:100833. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100833. eCollection 2023 Dec. Mater Today Bio. 2023. PMID: 37920293 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barzegar, P. E. F. , Ranjbar, R. , Yazdanian, M. , Tahmasebi, E. , Alam, M. , Abbasi, K. , Tebyaniyan, H. , & Esmaeili Fard Barzegar, K. (2022). The current natural/chemical materials and innovative technologies in periodontal diseases therapy and regeneration: A narrative review. Materials Today Communications, 32, 104099.
-
- Beahm, E. K. , Walton, R. L. , & Patrick, C. W. (2003). Progress in adipose tissue construct development. Clinics in Plastic Surgery, 30(4), 547–558. - PubMed
-
- Cigna, E. , Tarallo, M. , Bistoni, G. , Anniboletti, T. , Trignano, E. , Tortorelli, G. , & Scuderi, N. (2009). Evaluation of polyurethane dressing with ibuprofen in the management of split‐thickness skin graft donor sites. In Vivo (Athens, Greece), 23(6), 983–986. - PubMed
-
- El‐Ashram, S. , El‐Samad, L. M. , Basha, A. A. , & El Wakil, A. (2021). Naturally‐derived targeted therapy for wound healing: Beyond classical strategies. Pharmacological Research, 170, 105749. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

