Effect of intermittent mild cold stimulation on intestinal immune function and the anti-stress ability of broilers
- PMID: 36571877
- PMCID: PMC9803957
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102407
Effect of intermittent mild cold stimulation on intestinal immune function and the anti-stress ability of broilers
Abstract
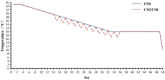
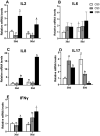
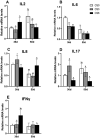
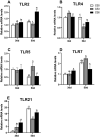
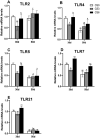
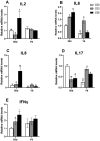
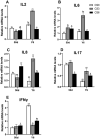
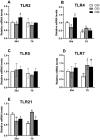
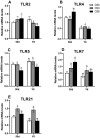
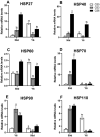
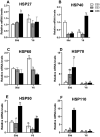
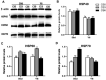
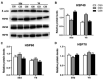
A total of 240 healthy 1-day-old Ross 308 male broilers were randomly divided into 3 groups (CS0 group, CS3 group, and CS6 group), with 5 replicates in each group and 16 broilers in each replicate, in order to evaluate the effects of intermittent mild cold stimulation (IMCS) on the intestinal immune function and anti-cold stress ability of broilers after acute cold stress. The mRNA expression levels of cytokines and Toll-like receptors (TLRs) in the duodenum and jejunum were detected at the end of cold stimulation (36 d), 2 wk after recovery (50 d), and after acute cold stress (Y6). In addition, the mRNA and protein expression levels of heat shock proteins (HSPs) were measured before and after acute cold stress. The experimental data were statistically processed using 1-way ANOVA and Duncan's multiple comparisons. The results showed that the mRNA expression levels of IL2, IL8, IFN γ, TLR7, and TLR21 in the duodenum and IL2 and IFN γ in jejunum were significantly higher in the CS6 group than in the CS0 and CS3 groups at 36 d (P < 0.05). All TLR levels in the jejunum were significantly lower in the CS3 group than in the CS0 and CS6 groups at 36 d (P < 0.05). After 6 h of acute cold stress, in the duodenum, the mRNA expression levels of IL6 and IL8 were significantly decreased in the CS0 and CS6 groups compared to levels at 50 d (P < 0.05), while levels in the CS3 group remained stable (P > 0.05). Compared with 50 d, the expression level of HSP mRNA in the jejunum in the CS3 group was relatively stable compared to that in the CS0 and CS6 groups after acute cold stress (P > 0.05). At the protein level, the HSP60 expression level in the duodenum and HSP40, HSP60, and HSP70 expression levels in the jejunum were significantly higher in the CS3 group than in the CS0 and CS6 groups after acute cold stress (P < 0.05). In conclusion, cold stimulation training at 3℃/3 h lower than the conventional feeding temperature can improve the intestinal immune function and anti-stress ability of broilers.
Keywords: broiler; cold adaptation; immune regulation; intermittent mild cold stimulation; small intestine.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intermittent mild cold stimulation improves the immunity and cold resistance of spleens in broilers.Poult Sci. 2021 Dec;100(12):101492. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.101492. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Poult Sci. 2021. PMID: 34695632 Free PMC article.
-
Intermittent mild cold acclimation ameliorates intestinal inflammation and immune dysfunction in acute cold-stressed broilers by regulating the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway.Poult Sci. 2024 May;103(5):103637. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103637. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 38518665 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of mild intermittent cold stimulation on thymus immune function in broilers.Poult Sci. 2022 Oct;101(10):102073. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102073. Epub 2022 Jul 27. Poult Sci. 2022. PMID: 36058173 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of naturally oxidized corn oil on inflammatory reaction and intestinal health of broilers.Poult Sci. 2022 Jan;101(1):101541. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.101541. Epub 2021 Oct 13. Poult Sci. 2022. PMID: 34788712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term music stimulating alleviated the inflammatory responses caused by acute noise stress on the immune organs of broilers by NF-κB signaling pathway.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024 Mar 15;273:116131. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116131. Epub 2024 Feb 26. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024. PMID: 38412629 Review.
References
-
- Abdel-Mageed A.M., Isobe N., Yoshimura Y. Effects of different TLR ligands on the expression of proinflammatory cytokines and avian β-defensins in the uterine and vaginal tissues of laying hens. Vet. Immunol. Immunop. 2014;162:132–141. - PubMed
-
- Al-Zghoul M.B., Saleh K.M., Ababneh M.M.K. Effects of pre-hatch thermal manipulation and post-hatch acute heat stress on the mRNA expression of interleukin-6 and genes involved in its induction pathways in 2 broiler chicken breeds. Poult. Sci. 2019;98:1805–1819. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee S.K., Aviles H., Fox M.T., Monroy F.P. Cold stress-induced modulation of cell immunity during acute Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice. J. Parasitol. 1999;85:442–447. - PubMed
-
- Basu M., Paichha M., Swain B., Lenka S.S., Singh S., Chakrabarti R., Samanta M. Modulation of TLR2, TLR4, TLR5, NOD1 and NOD2 receptor gene expressions and their downstream signaling molecules following thermal stress in the Indian major carp catla (Catla catla) 3 Biotech. 2015;5:1021–1030. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

