Altered sulfation status of FAM20C-dependent chondroitin sulfate is associated with osteosclerotic bone dysplasia
- PMID: 36572689
- PMCID: PMC9792594
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-35687-3
Altered sulfation status of FAM20C-dependent chondroitin sulfate is associated with osteosclerotic bone dysplasia
Abstract
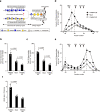
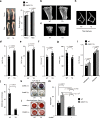
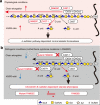
Raine syndrome, a lethal osteosclerotic bone dysplasia in humans, is caused by loss-of-function mutations in FAM20C; however, Fam20c deficiency in mice does not recapitulate the human disorder, so the underlying pathoetiological mechanisms remain poorly understood. Here we show that FAM20C, in addition to the reported casein kinase activity, also fine-tunes the biosynthesis of chondroitin sulfate (CS) chains to impact bone homeostasis. Specifically, FAM20C with Raine-originated mutations loses the ability to interact with chondroitin 4-O-sulfotransferase-1, and is associated with reduced 4-sulfation/6-sulfation (4S/6S) ratio of CS chains and upregulated biomineralization in human osteosarcoma cells. By contrast, overexpressing chondroitin 6-O-sulfotransferase-1 reduces CS 4S/6S ratio, and induces osteoblast differentiation in vitro and higher bone mineral density in transgenic mice. Meanwhile, a potential xylose kinase activity of FAM20C does not impact CS 4S/6S ratio, and is not associated with Raine syndrome mutations. Our results thus implicate CS 4S/6S ratio imbalances caused by FAM20C mutations as a contributor of Raine syndrome etiology.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

