Current Trends in the Utilization of a Robotic Approach in the Field of Bariatric Surgery
- PMID: 36572836
- PMCID: PMC9792156
- DOI: 10.1007/s11695-022-06378-1
Current Trends in the Utilization of a Robotic Approach in the Field of Bariatric Surgery
Abstract
Purpose: The utilization rate of robotic surgery for bariatric procedures is not well-described. Our study identified the proportion of metabolic and bariatric surgery (MBS) procedures in the United States between 2015 and 2020 performed using a robotic (R-) or laparoscopic (L-) approach.
Materials and methods: A descriptive analysis of the 2015-2020 Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program (MBSAQIP) Participant User Data File (PUF) datasets was performed. The primary outcome was (1) surgical cases performed annually and (2) proportion of cases performed using a R- or L- approach. Analysis was done separately for sleeve gastrectomy (SG), Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB), biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD-DS), and revisional bariatric surgery (RBS). Statistical analysis consisted of means and proportions, fold difference, annual slope, and Student's t tests or chi-square tests as appropriate, with statistical significance set to p < .05.
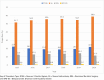
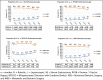
Results: A total of 1,135, 214 procedures were captured between 2015 and 2020. R-RYGB increased from 2554 to 6198 (6.8% to 16.7%), R-SG increased from 5229 to 17,063 (6.0% to 17.2%), R-RBS increased from 993 to 3386 (4.7% to 17.4%), and R-BPD-DS increased from 221 to 393 (22.0% to 28.4%). The greatest annual increase was observed among R-RBS and R-SG (3.70-fold difference; slope 2.4% per year and 2.87-fold difference; slope 2.2% per year, respectively).
Conclusion: There is a nationwide increase in the utilization of a R- approach in bariatric surgery. There are concerns related to the potential increase in healthcare expenditures related to robotics. Further studies are needed to establish key performance indicators along with guidelines for training, adoption and utilization of a R- approach.
Keywords: Bariatric surgery; Bariatrics; Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch; Duodeno-ileostomy; Laparoscopy; Revisional bariatric surgery; Robotic utilization; Robotics; Roux-en-Y gastric bypass; Sleeve gastrectomy.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Wayne B. Bauerle, Pooja Mody, Allison Estep, and Jill Stoltzfus declare no competing interests. Maher El Chaar is a consultant at Intuitive Surgical and receives honoraria for lectures, presentations, and educational events.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials