CCNE1 and survival of patients with tubo-ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma: An Ovarian Tumor Tissue Analysis consortium study
- PMID: 36572991
- PMCID: PMC10107112
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.34582
CCNE1 and survival of patients with tubo-ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma: An Ovarian Tumor Tissue Analysis consortium study
Abstract
Background: Cyclin E1 (CCNE1) is a potential predictive marker and therapeutic target in tubo-ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma (HGSC). Smaller studies have revealed unfavorable associations for CCNE1 amplification and CCNE1 overexpression with survival, but to date no large-scale, histotype-specific validation has been performed. The hypothesis was that high-level amplification of CCNE1 and CCNE1 overexpression, as well as a combination of the two, are linked to shorter overall survival in HGSC.
Methods: Within the Ovarian Tumor Tissue Analysis consortium, amplification status and protein level in 3029 HGSC cases and mRNA expression in 2419 samples were investigated.
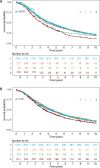
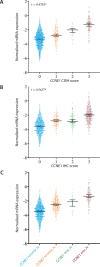
Results: High-level amplification (>8 copies by chromogenic in situ hybridization) was found in 8.6% of HGSC and overexpression (>60% with at least 5% demonstrating strong intensity by immunohistochemistry) was found in 22.4%. CCNE1 high-level amplification and overexpression both were linked to shorter overall survival in multivariate survival analysis adjusted for age and stage, with hazard stratification by study (hazard ratio [HR], 1.26; 95% CI, 1.08-1.47, p = .034, and HR, 1.18; 95% CI, 1.05-1.32, p = .015, respectively). This was also true for cases with combined high-level amplification/overexpression (HR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.09-1.47, p = .033). CCNE1 mRNA expression was not associated with overall survival (HR, 1.00 per 1-SD increase; 95% CI, 0.94-1.06; p = .58). CCNE1 high-level amplification is mutually exclusive with the presence of germline BRCA1/2 pathogenic variants and shows an inverse association to RB1 loss.
Conclusion: This study provides large-scale validation that CCNE1 high-level amplification is associated with shorter survival, supporting its utility as a prognostic biomarker in HGSC.
Keywords: CCNE1 amplification; cyclin E1 expression; high-grade serous carcinoma; ovarian cancer; prognosis.
© 2022 The Authors. Cancer published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Cancer Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest regarding this publication. A. Hartmann has received honoraria from BMS, MSD, Roche, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, AbbVie, Jansen‐Cilag, and Ipsen.
T.P. Conrads is member of the Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc scientific advisory board. P.A. Cohen is a member of the Clinic IQ Scientific Advisory Board and has received honoraria from Seqirus and Astra Zeneca. D. Bowtell has research funding from AstraZeneca, Beigene, and Genentech Roche, and is an advisor to Exo Therapeutics. U. Menon has received an honorarium from the NY Obstetrical Society and held personal shares between 1 April 2011 and 30 October 2021. T. Van Gorp has received honoraria for advisory boards from Eisai Europe (to institute), OncXerna Therapeutics (to institute), Astra Zeneca (to institute), GSK (to institute), MSD (to institute), research funding from Amgen (to institute), Roche (to institute), and AstraZeneca (to institute) and travel reimbursements from MSD, Immunogen, PharmaMar, and AstraZeneca. P. Harter has received honoraria from Amgen, AstraZeneca, GSK, Roche, Sotio, Stryker, Zai Lab, MSD, Clovis, and Eisai; has served on advisory boards for AstraZeneca, Roche, GSK, Clovis, Immunogen, MSD, and Eisai; and has received research funding (to institute) from AstraZeneca, Roche, GSK, Genmab, DFG, European Union, DKH, Immunogen, and Clovis. P. Ghatage has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, GSK, and Eisai. I. Vergote has received consulting fees from Agenus, Akesobio, AstraZeneca, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Deciphera Pharmaceuticals, Eisai, Elevar Therapeutics, F. Hoffmann‐La Roche, Genmab, GSK, Immunogen, Jazzpharma, Karyopharm, Mersana, MSD, Novocure, Novartis, Oncoinvent, OncXerna, Sanofi, Seagen, Sotio, Verastem Oncology, and Zentalis, done contracted research with Oncoinvent AS and corporate sponsored research with Amgen and Roche, and received travel expenses/accommodations from Karyopharm and Genmab. D. Bowtell has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, has a consulting role with Exo Therapeutics Research and receives funding from Roche/Genentech, AstraZeneca and BeiGene. A. DeFazio received grant funding from AstraZeneca. A.H. had an advisory role and received honoraria from BMS, MSD, Roche, Cepheid, Qiagen, Agilent, Diaceutics, Lilly, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, AbbVie, Jansen‐Cilag, Pfizer, and Ipsen. R. Erber has received honoraria from Roche, Eisai, Pfizer, BioNTech, Veracyte (PROCURE), Diaceutics, and Novartis. The institution of A. Hartmann and R. Erber conducts research for AstraZeneca, Roche, Janssen‐Cilag, NanoString Technologies, Biocartis, ZytoVision, Novartis, Cepheid, and BioNTech. S. Heublein received honoraria from Clovis, Merck Sharp & Dohme Corporation and Pfizer, and has received research funding from Neuer Stiftung fuer Medizische Forschung and Novartis as well as travel support from GlaxoSmithKline.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA172404/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA047904/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA243483/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 15601/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- M01 RR000056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA095023/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K07 CA080668/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA172404/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014089/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_00004/01/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 CA122443/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA243483/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA160669/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA248288/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 22905/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA243511/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA071789/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA136393/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA210210/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA015083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

