Implementation of a psychological online intervention for low to moderate depression in primary care: study protocol
- PMID: 36573071
- PMCID: PMC9789354
- DOI: 10.1016/j.invent.2022.100581
Implementation of a psychological online intervention for low to moderate depression in primary care: study protocol
Abstract
Background: Depression affects millions of people all over the world and implies a great socioeconomic burden. Despite there are different effective evidence-based interventions for treating depression, only a small proportion of these patients receives an appropriate treatment. In this regard, information and communication technologies (ICTs) can be used with therapeutic aims and this can contribute to make interventions more accessible. One example is "Smiling is fun", an internet-based treatment which has proved to be effective and cost-effective for treating depression in Spanish Primary Care (PC). However, the "know-do gap" between research and clinical settings implies that the actual implementation of such interventions could last up to 20 years. To overcome this obstacle, the implementation research establishes the methodology to implement the advances developed in the laboratories to the health care services maintaining the validity of the intervention and offering specific strategies for the implementation process.
Objective: This is the protocol of an implementation study for the Internet-based program "Smiling is fun", which will be conducted on patients with mild-to-moderate depression of Spanish PC settings. In the implementation study, the feasibility, efficacy, cost-efficacy, acceptability, adoption, appropriateness, fidelity, penetration, normalization, and sustainability will be assessed.
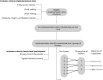
Methods: The current investigation is a Hybrid Effectiveness-Implementation Type II design. A Stepped Wedge randomized controlled trial design will be used, with a cohort of 420 adults diagnosed with depression (mild-to-moderate) who will undergo a first control phase (no treatment) followed by the intervention, which will last 16 weeks, and finishing with an optional use of the intervention. All patients will be assessed at baseline, during the treatment, and at post-treatment. The study will be conducted in three Spanish regions: Andalusia, Aragon, and the Balearic Islands. Two primary care centers of each region will participate, one located in the urban setting and the other in the rural setting. The primary outcome will be implementation success of the intervention assessing the reach, clinical effect, acceptability, appropriateness, adoption, feasibility, fidelity, penetration, implementation costs and sustainability services.
Discussion: "Smiling is Fun", which has already been established as effective and cost-effective, will be adapted according to users' experiences and opinions, and the efficacy and cost-efficacy of the program will again be assessed. The study will point out barriers and facilitators to consider in the implementation process of internet-based psychological interventions in health services. The ultimate goal is to break the research-to-practice split, which would undoubtedly contribute to reduce the high burden of depression in our society.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, Identifier: NCT05294614.
Keywords: Depression; Evidence-based treatment; Health settings; Implementation; Primary care; Psychological treatment.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
Publication types
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

